Tutorial: Subcutaneous Solution Injection
Open GPX™ and, in the Dashboard view, click on the icon next to Select to open an Existing project.
Click Browse and navigate to the C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Simulations Plus, Inc\GastroPlus\10.2\Tutorials\Midazolam-SubQ folder and select the project file Midazolam-SubQ.gpproject by clicking on it and clicking Open.
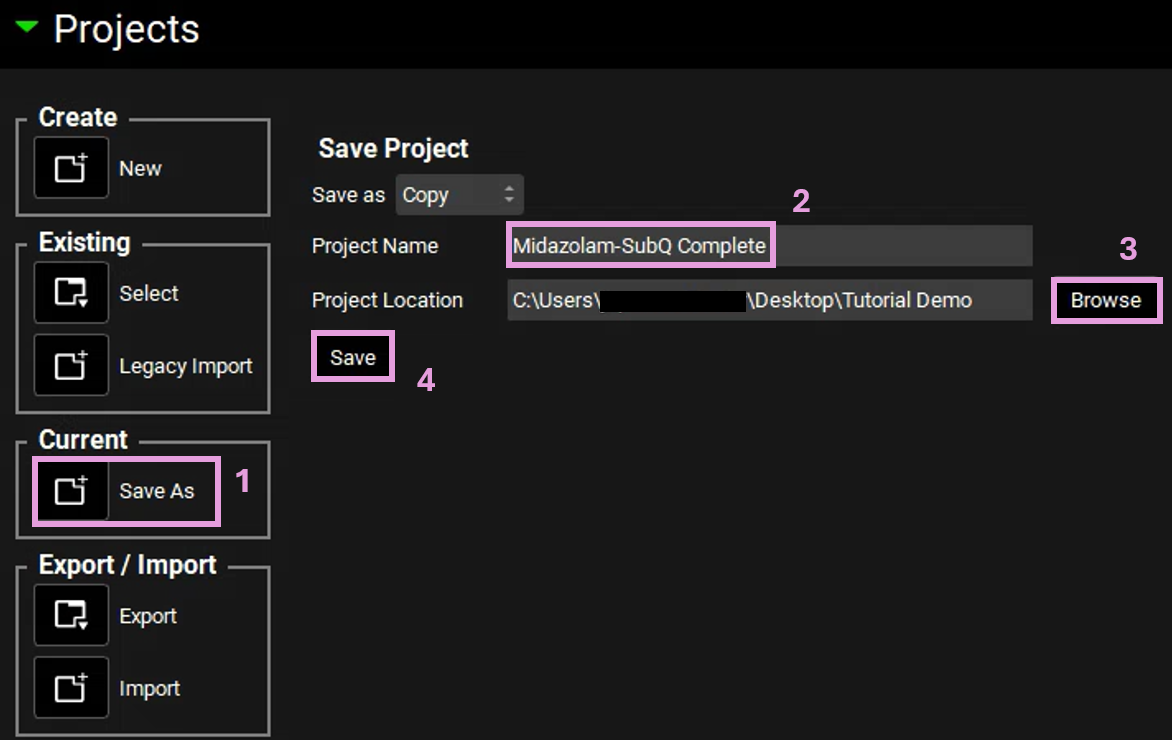
Save a copy of the project by clicking on the icon next to Save As, entering “Midazolam-SubQ Complete” as the Project Name and click Browse to navigate to/add a folder to Save the project in. You will see an information message in the Messages Center indicating that the project has been successfully copied. This message will disappear once you click 'Yes' on the pop-up window. Note that the name of the project visible in the top right corner of the interface is the one that has just been created.
Move through the views on the navigation pane from Observed Data to Simulations, observing the information that has been entered into this project. You will see that there is a PBPK model for 85.53kg HumanFasted physiology in the Pharmacokinetics view and simulations set up for Midazolam (Midazolam Pecking IV and Midazolam15mg NoGFJ).
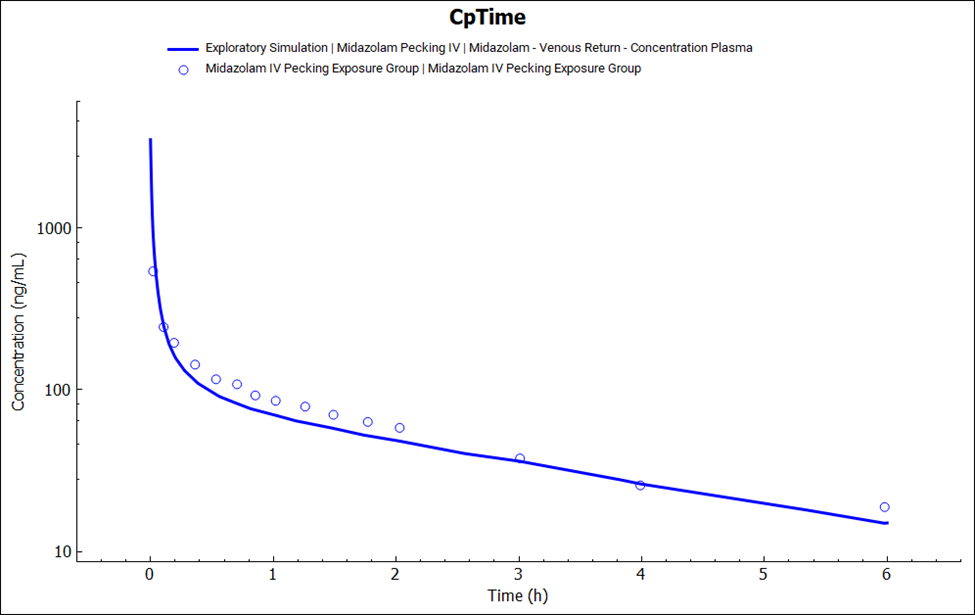
In the Simulations view, select the “Midazolam Pecking IV” from the simulation drop-down and click on Run Simulation.
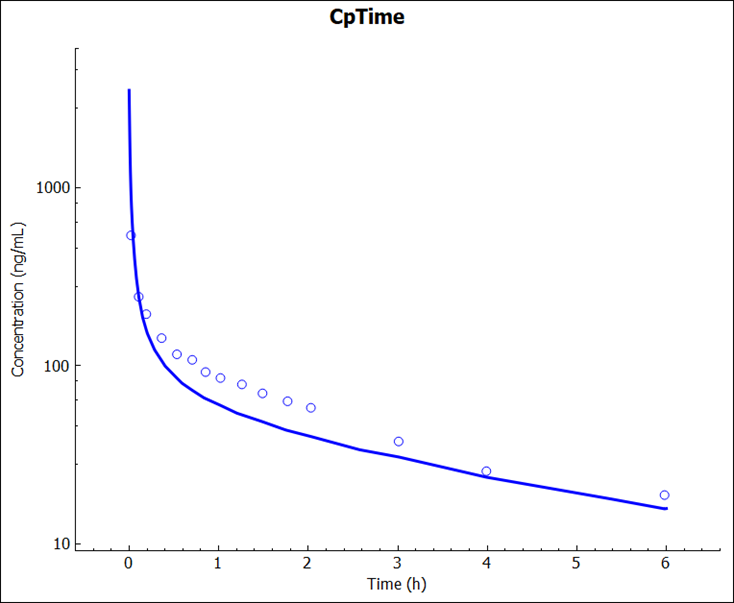
Once the simulation finishes, the program switches automatically to the Analysis view. The CpTime plot will be displayed in the Key View mode. Observe the result in semi-log scale.
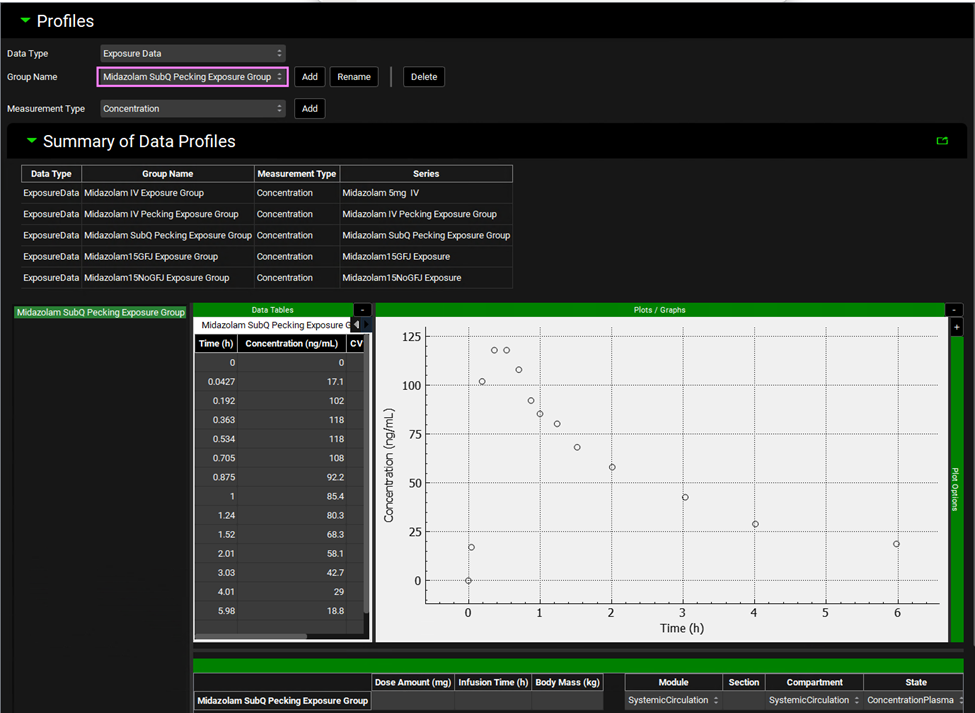
Next, we will set up the simulation for subcutaneous dosing. Navigate to the Observed Data view and review the experimental Cp-time data in the Midazolam SubQ Pecking Exposure Group.
Navigate to the Dosing view and expand the Formulations panel by double clicking on the panel header or clicking on the green arrow. Click on “Add” next to the drop-down and the Enter Formulation name in the dialog box that opens. Name the formulation asset “SQ Solution Abdomen” and click OK.
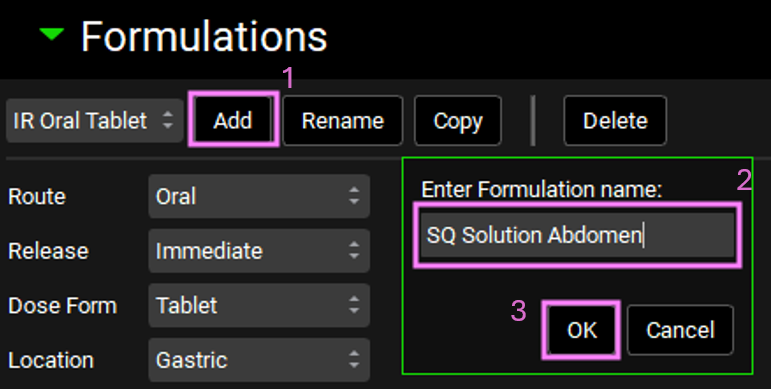
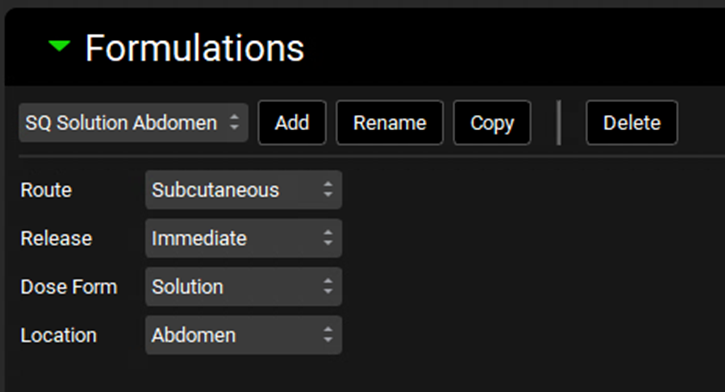
Set the route to Subcutaneous, the release to Immediate, the Dose Form to Solution, and the location to Abdomen.
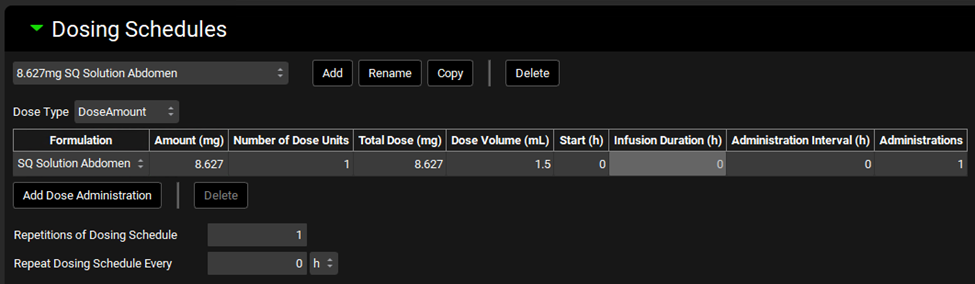
Expand the Dosing Schedules panel by double clicking on the panel header or clicking on the green arrow. Add a new Dosing Schedule and name it 8.627mg SQ Solution Abdomen and click OK. Select the SQ Solution Abdomen formulation and set the amount to 8.627 mg and the dose volume to 1.5 mL.
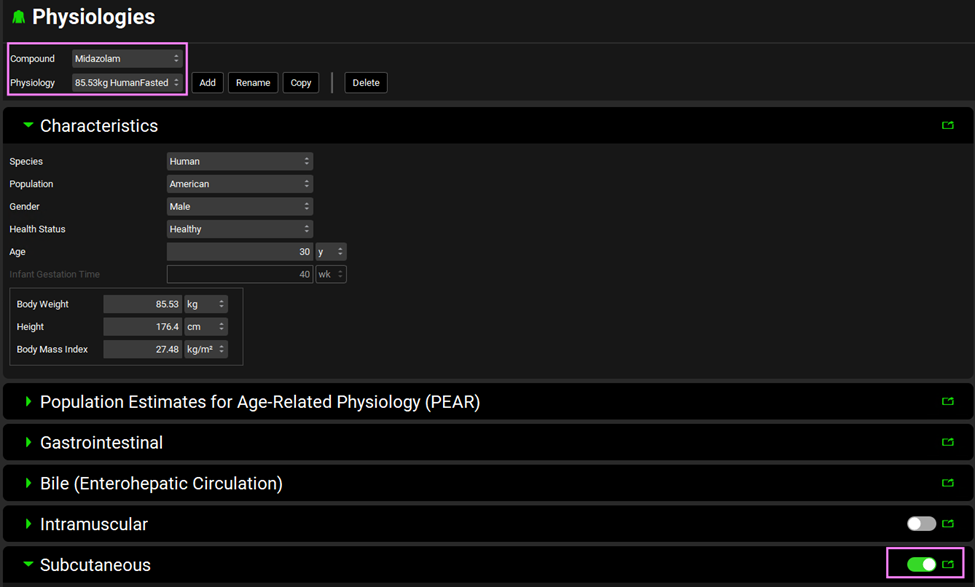
Go to the Physiologies panel and select the 85.53 kg HumanFasted physiology from the drop-down menu. Make sure “Midazolam” compound is selected. Scroll down to the Subcutaneous panel and click on the panel toggle to enable the Subcutaneous route.
Click on the Add Tissue drop-down and select Abdomen. The Abdomen administration site will appear in the diagram. Expand the Compound sub-panel and change the Fu Tissue to 0.028 (which corresponds to the value estimated for adipose Fut in the PBPK model).
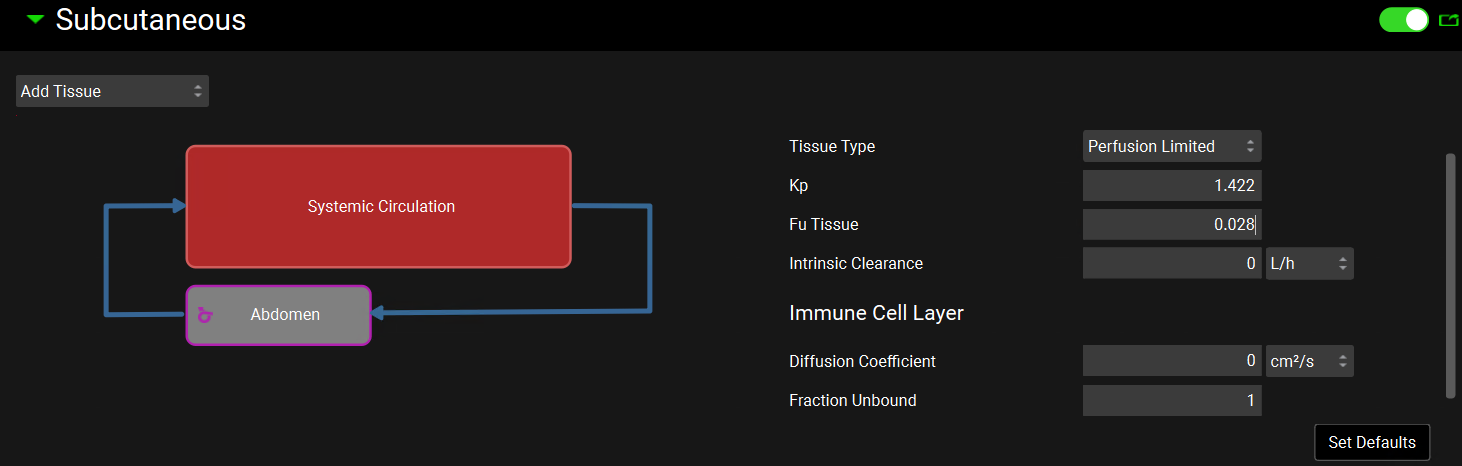
The sub-panels on the right-hand side are only shown when the tissue box is selected. You can scroll down to the Physiology sub-panel to see the blood flow at the injection site. In fasting humans, subcutaneous abdominal blood flow can increase by 45% in non-obese subjects 1 . The blood flow rate was automatically set to reflect this change.
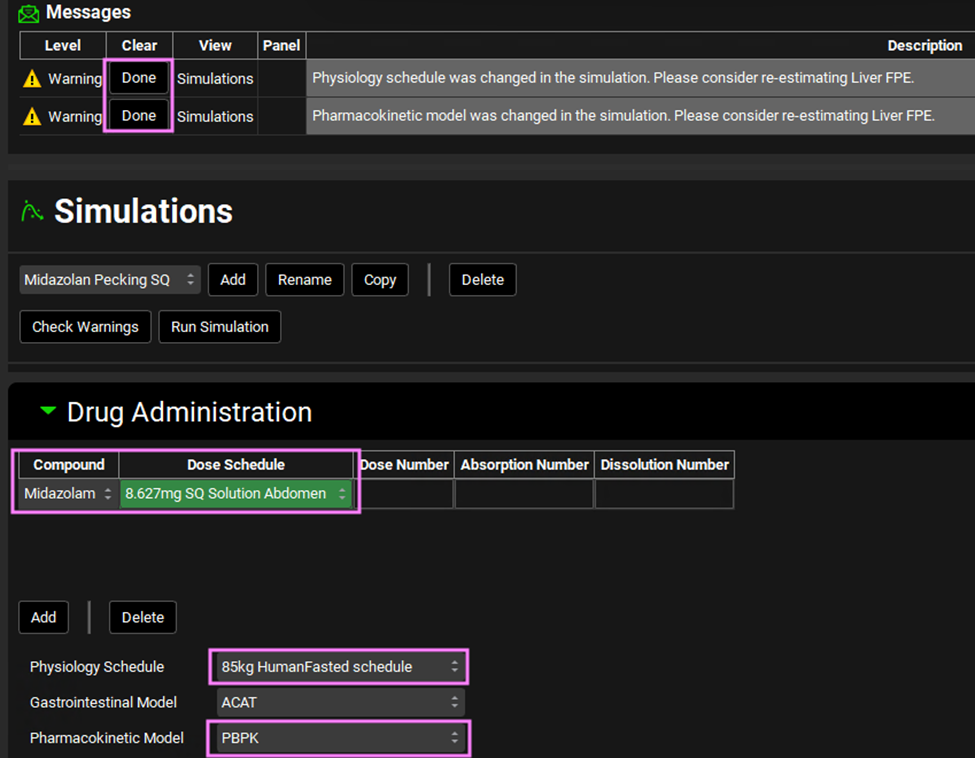
Save the project and navigate to the Simulations view. Click on Add next to the simulations drop-down. The Enter Simulation name: dialog box will open. Name the simulation “Midazolam Pecking SQ” and click OK or press Enter. In the Drug Administration panel, set the compound to Midazolam and set the Dose Schedule to the 8.627mg SQ Solution Abdomen Dose Schedule, the physiology schedule to 85kg HumanFasted schedule, and the pharmacokinetic model to PBPK. Click Done on the messages that come up in the Messages center.
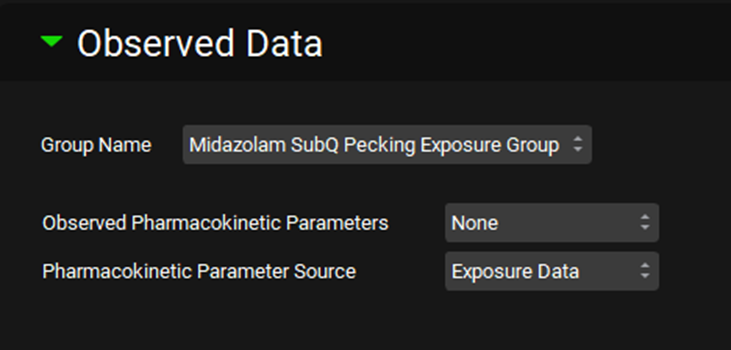
Expand the Compound Settings and scroll down to the Observed Data sub-panel and select the Midazolam SubQ Pecking Exposure Group from the Group Name drop-down.
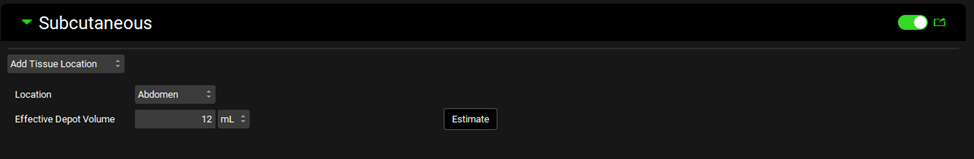
Scroll down to the Additional Dosage Routes panel and expand it. Click on the Subcutaneous sub-panel toggle to enable the Subcutaneous model and expand the sub-panel. Click on the Add Tissue Location drop-down menu and select Abdomen. Update the Effective Depot Volume to 12 mL. Check Warnings and run a simulation.
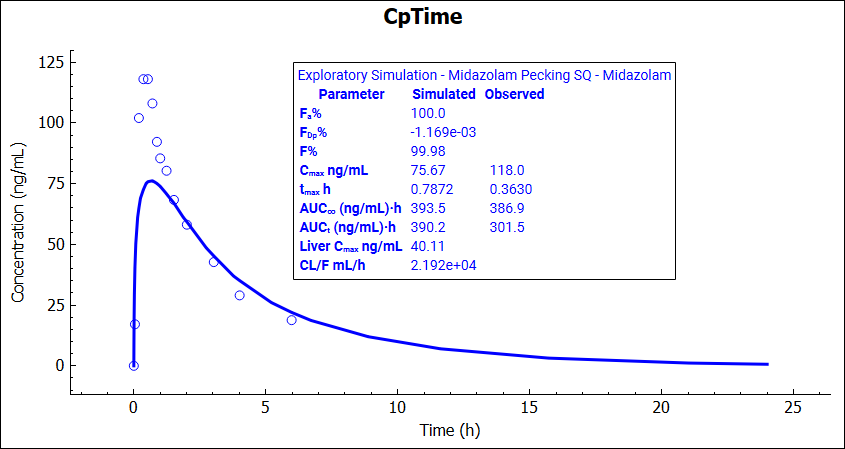
The simulations results can be displayed on the graph by clicking on the Additional Features panel.
Let’s explore the effect of the subcutaneous partition coefficient on the drug appearance in plasma after subcutaneous administration. Navigate back to the Physiologies view. Expand the Subcutaneous panel and set the Kp to 0.8 in the Compound sub-panel.
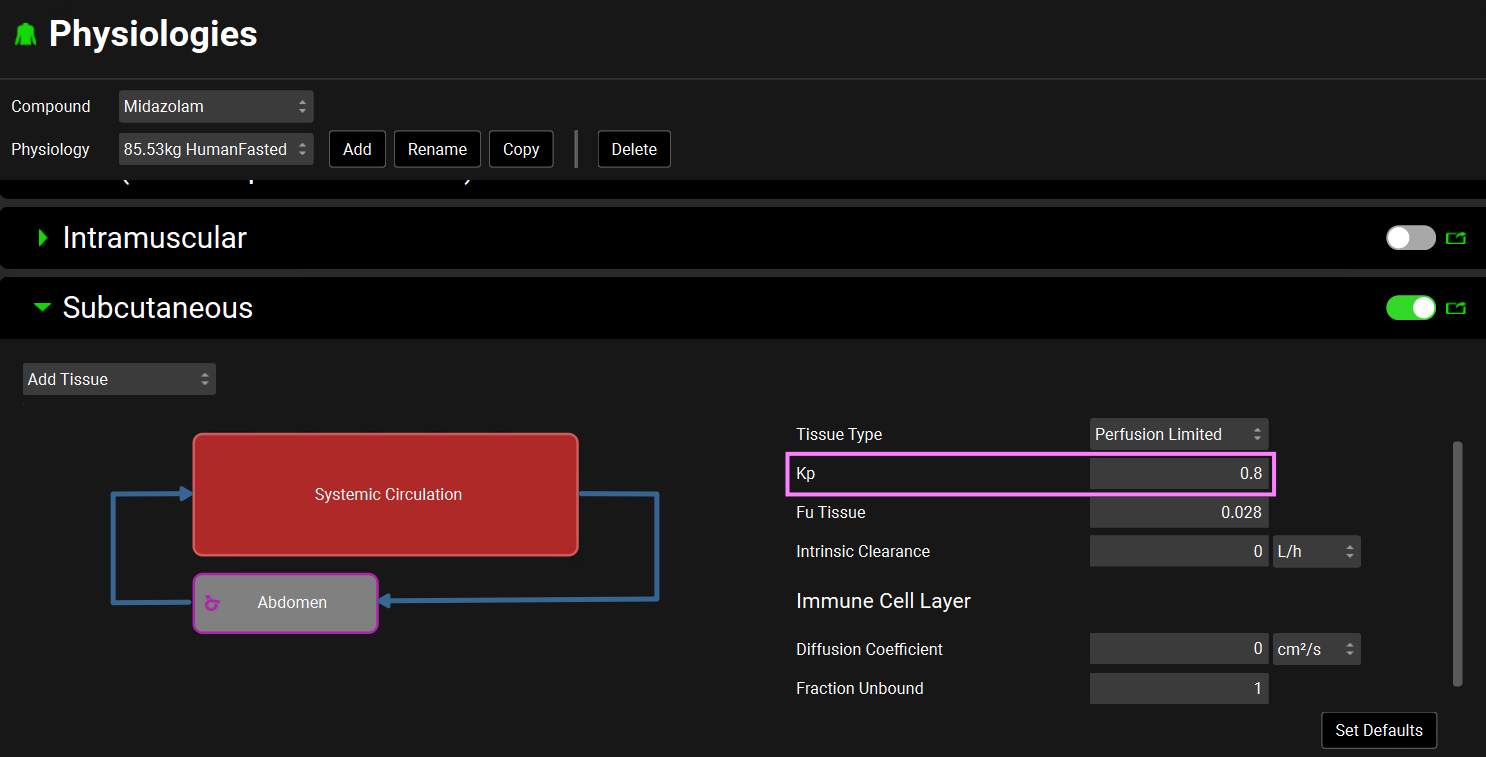
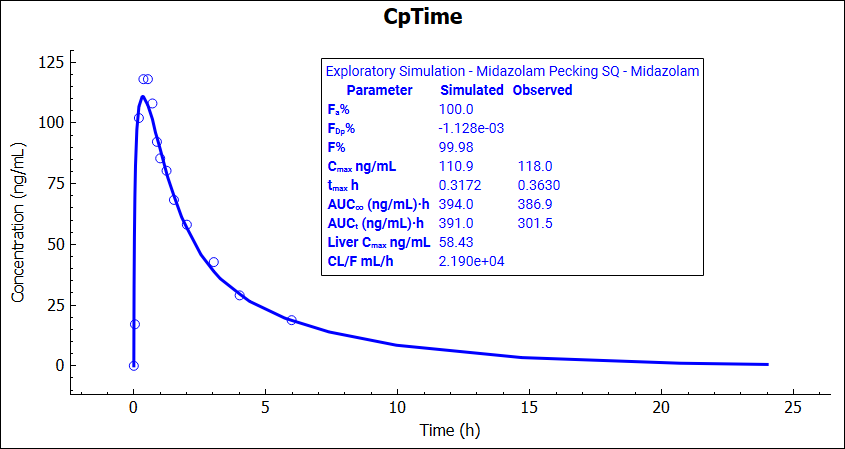
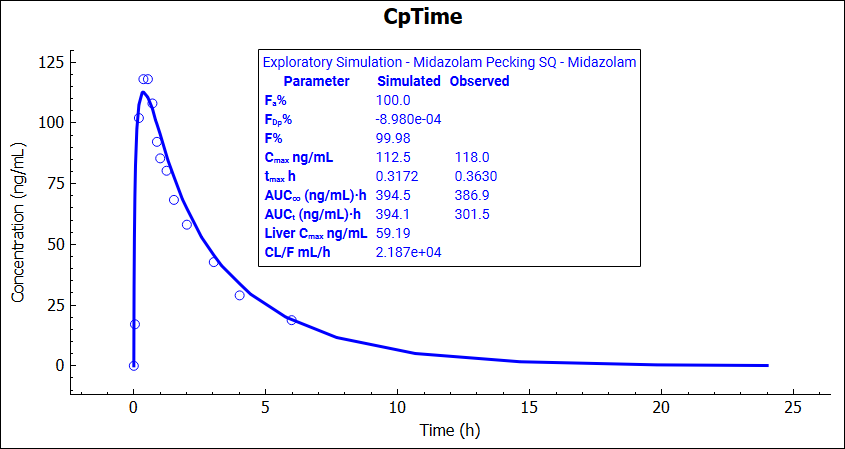
Navigate to the Simulations view again and run the Midazolan Pecking SQ simulation (which is now using the updated subcutaneous Kp). Note that the simulated Cmax is now very close to the observed value.
The Kp at the subcutaneous injection site is expected to be the same as the Kp for the Adipose compartment in the PBPK model. Navigate to the Pharmacokinetics view and change the Adipose Kp to 0.8 in the PBPK model.
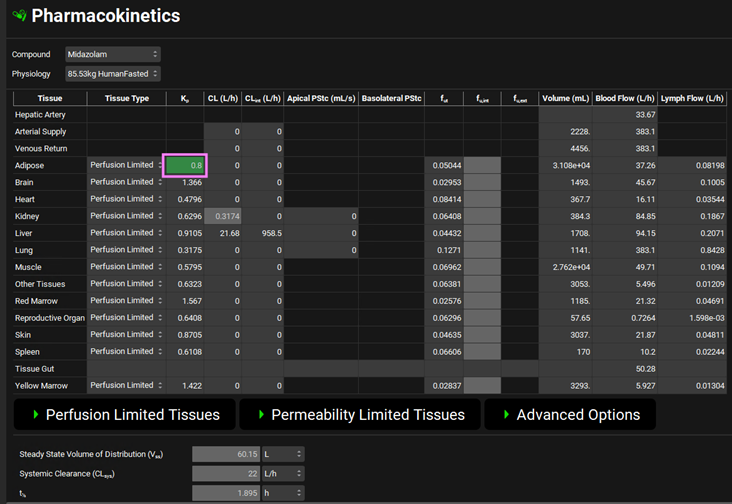
Navigate to Simulations view and run Midazolam Pecking IV and Midazolam Pecking SQ respectively. Explore the simulation results for subcutaneous and intravenous dosing.
- Engfeldt, P. and Linde, B. (1992). “Subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow in the abdominal and femoral regions in obese women: effect of fasting.” Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 16(11): 875-9.
