GPX™ Run Modes Tutorial: Replicate Virtual Bioequivalence: 4-Period, 2-Sequence, and 2-Treatment Bioequivalence Study of Metformin
Open GPX™ and, in the Dashboard view, click on the icon next to Select to open an Existing project.
Click Browse and navigate to the C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Simulations Plus,Inc\GastroPlus\10.2\Tutorials\Replicate Design folder and select the project file “Metformin replicated VBE Case Study.gpproject” by clicking on it and clicking Open.
Select Observed Data on the navigation pane. Look at the in vitro dissolution profiles and the exposure data for the test and reference formulations.
Select the Dosing view on the navigation pane. The test and reference controlled-release formulations and dosing schedules have already been created as shown in the Tutorial: IVIVCPlus™ Module. Metformin is administered as a salt, with the free base accounting for 721 mg of the 1000 mg dose. Therefore, the dosing schedule is based solely on the free base amount.
Select the Physiologies view on the navigation pane and review the American 30 yo 85.53 kg physiology.
Select the Simulations view on the navigation pane. Create the Test Simulation by clicking on Add and name it “Test”. Clear the information message in the Messages center indicating that for the compound the transcellular Peff is set to zero.
Under Drug Administration, select:
Compound: Metformin
Dose Schedule: 1000 mg PO SD XR Test
Pharmacokinetic Model: PBPK
Under Compound Settings and Observed Data, select:
Group Name: Test
Copy the Test simulation to create the Reference simulation. Make sure the selected Dose Schedule and Observed Data corresponds to the reference formulation (these reusable assets have already been created).
Run both Test and Reference simulations and observe the simulations results in the Analysis view.
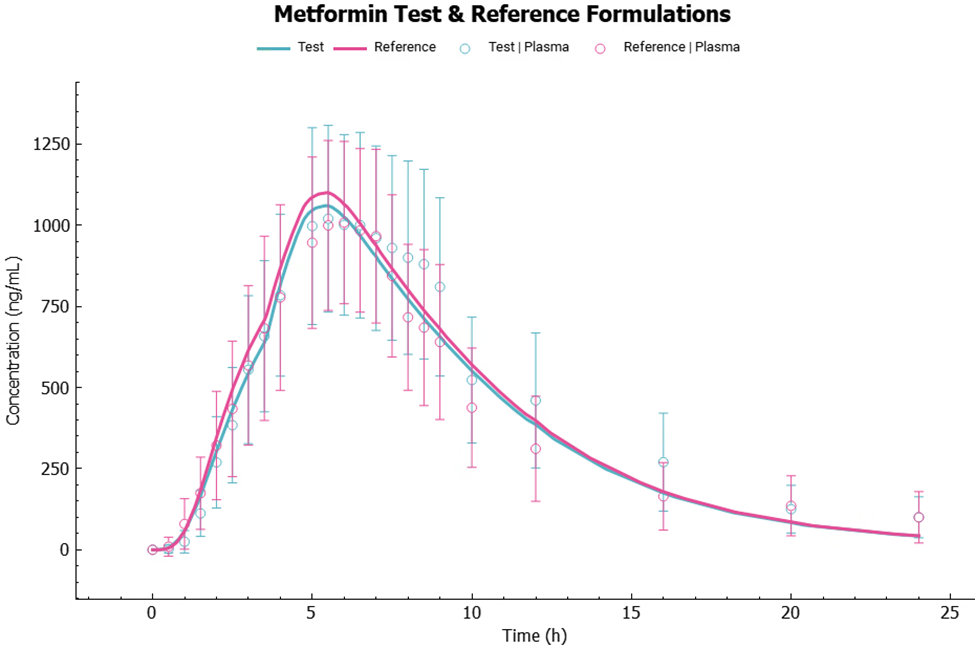
Now that we have demonstrated that the Metformin PBPK model can predict well the Cp-time profiles following the test and reference single administration, we can use it to do a virtual bioequivalence analysis. (Note: The replicate design is usually applied to high variable drugs.)
To set up the VBE analysis, do the following steps:
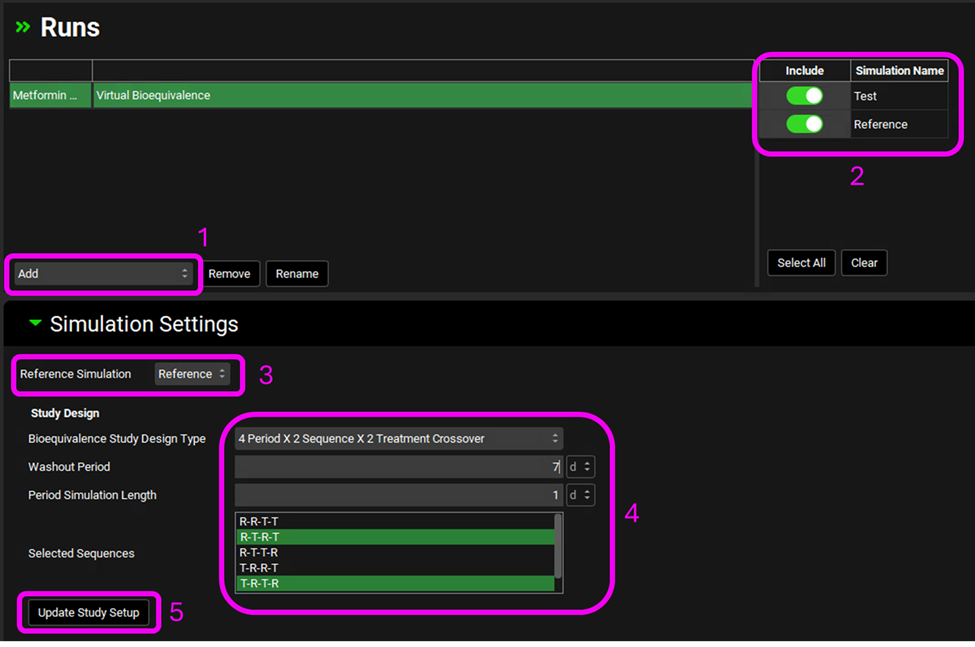
· Go to the Runs view and click Add. Select Virtual Bioequivalence and name it Metformin VBE
· Include both simulations: Reference and Test
· Select Reference for the Reference simulation
· Study Design: 4 Period, 2 Sequence, 2 Treatment Crossover
· Washout Period: 7 days
· Period Simulation Length: 1 day
· Sequences: RTRT and TRTR
· Click Update Study Setup (Note: By clicking this button, the program automatically creates the simulations, physiologies/regimen, doses/regimen that defines the study design.)
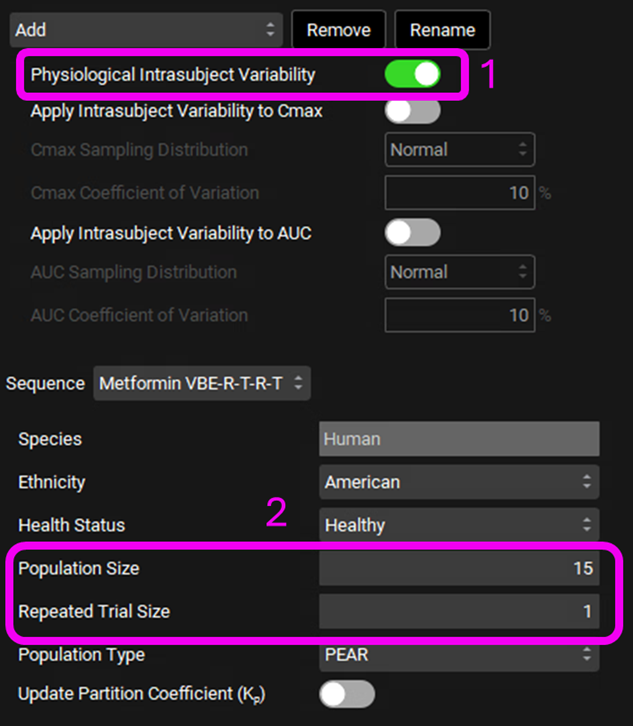
Select Physiological Intrasubject Variability.
Set the population size to 15 subjects and the number of trials to 1. Keep all other parameters as default values.
Run your VBE study by clicking on Start under the Run Controls panel.
Once the analysis is complete, check the result saved as an Excel document in your project directory (Excel file name: Bioequivalence Statistics).
You will notice differences between your VBE results and those presented below. This variation is due to the virtual population generation process using the PEAR algorithm, which produces a unique population for each simulation run.
VBE analysis is a computationally intensive process. If your system has less than 32 GB of RAM, the simulation may not complete when running via the graphical user interface. Consider running the VBE from Orchestrator (Execute a Virtual Bioequivalence Run), or using a virtual machine with more resources.
You can also set the cache data for Analysis to None in the Output Settings panel of your VBE Run. This setting is typically used to conserve memory for large populations or VBE runs, but it removes the ability to interactively review results within GPX. The only way to access results will be through the output files generated in your project directory, not through the GPX graphical user interface.
Additionally, you may temporarily reduce the number of subjects. Reducing subject count is intended solely to help complete this exercise and is not recommended for routine use.
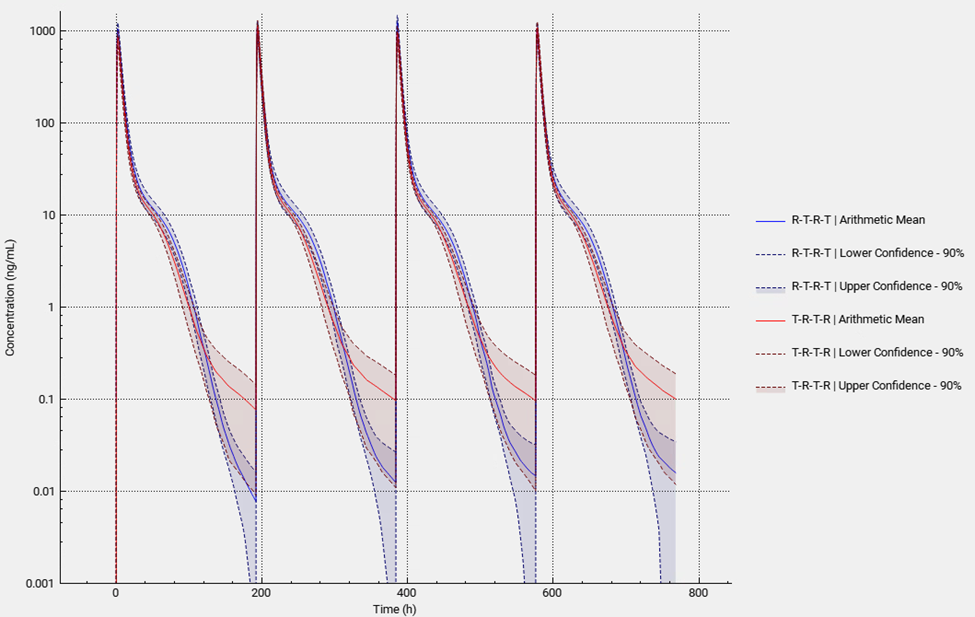
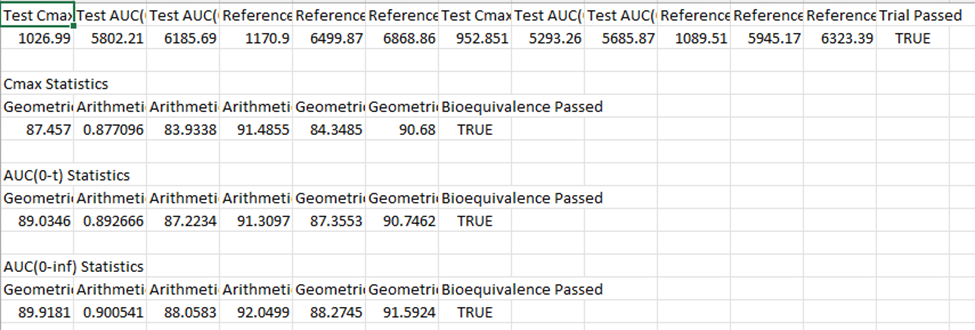
Using “User Defined Output Points” in the simulations included in the VBE run is a best practice to avoid differences in AUC, Cmax and Tmax between runs using the same population. This setting is found under “Configuration” panel in “Simulations” view.
