Pharmacokinetics View
The Pharmacokinetics view has two panels. All the inputs and options on the view and these two panels (and where applicable, their sub-panels) are described below. See:
The Distribution Dashboard is described as part of the PBPKPlus™ panel. See:
General Settings
Pharmacokinetics view
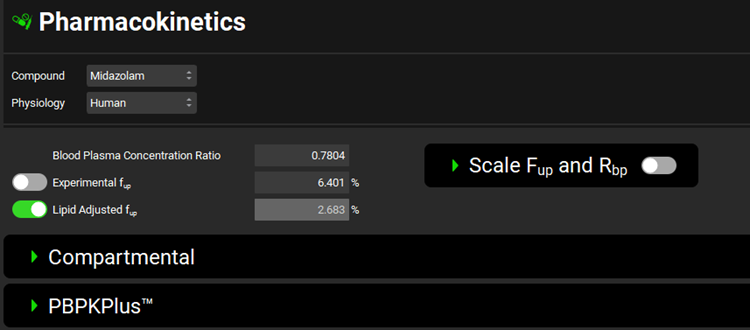
Input/Option | Description |
Compound | A drop-down. Selects the current compound. Options are populated based on compounds already added to the project. If no compounds have been added, this will be blank. If no compound is selected, the panels below will be disabled. |
Physiology | A drop-down. Selects the current physiology, populated based on physiologies added to the project. If no physiologies have been added, this will be blank. If no physiology is selected, the panels below will be disabled. |
Blood Plasma Concentration Ratio | The blood to plasma concentration ratio for the selected compound-physiology pair. The value can be edited. |
Experimental fup |
|
Lipid Adjusted fup |
Note: Experimental fup is used to calculate kidney filtration clearance when fup*GFR is selected as the method, regardless of the setting of the toggle above. Note: This fup adjustment assumes that Experimental fup is an accurate measure of drug binding to plasma proteins and that logP can be used as a measure of drug binding to plasma lipids. |
Scale Fup and Rbp sub-panel
The Scale Fup and Rbp sub-panel is used to determine whether the Experimental Fup and Blood Plasma Concentration Ratio (Rbp) are adjusted for different plasma protein and hematocrit levels in children or diseased populations. This adjustment assumes that the entered values of Rbp and Experimental Fup represent healthy adult parameters.
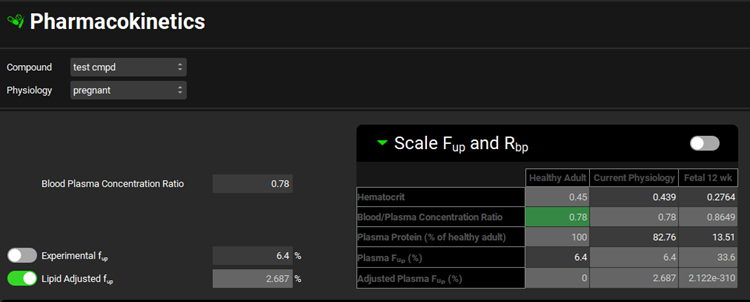
Pharmacokinetics view, Scale Fup and Rbp sub-panel, with toggle turned off
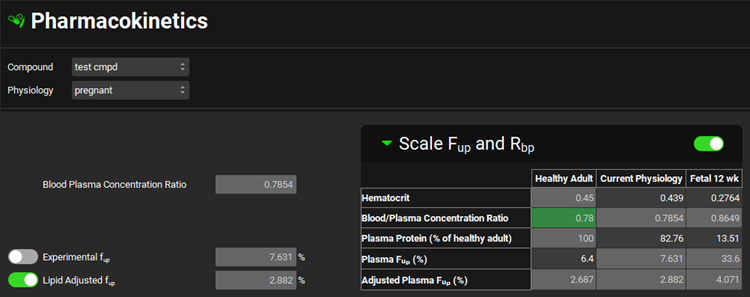
Pharmacokinetics view, Scale Fup and Rbp sub-panel, with toggle turned on
Input/Option | Description |
Scale Fup and Rbp | A toggle. Turned off by default. Must be turned on for specific populations to enable the scaling of the entered values of Rbp and Experimental Fup. When the toggle is turned off, there is no scaling of Rbp and Experimental Fup values, and those displayed in the Current Physiology column are identical to those in the general settings in the main view. When the toggle is turned on, the scaled values of Rbp and Experimental Fup are shown in the Current Physiology column and are also visible in the main view and cannot be edited. |
Scale Fup and Rbp table | Lists the relevant parameters (see below) for a Healthy Adult, in the left-hand column and the Current Physiology, in the right-hand column. If Scale Fup and Rbp is toggled off, the Fup and Rbp values in the Healthy Adult and Current Physiology columns will be identical. For Pregnant physiologies, the parameters for the fetus are also displayed. |
Hematocrit | Healthy Adult: The default hematocrit for a healthy adult. The value cannot be edited. Current Physiology /Fetal: The default hematocrit for the current physiology. The value can be edited. |
Blood/Plasma Concentration Ratio | Healthy Adult: The Rbp for the selected compound paired with a healthy adult physiology. The value can be edited if Scale Fup and Rbp is toggled On. Current Physiology / Fetal: The scaled Rbp for the scaled compound-physiology pair, calculated based on the difference in the hematocrit. The value can’t be edited. |
Plasma Protein (% of healthy adult) | Healthy Adult: The default amount of plasma protein, expressed as a percentage. The value can’t be edited. Current Physiology / Fetal: The default amount of plasma protein, for the current physiology, expressed as a percentage of the total plasma protein of a healthy adult. The value can be edited. |
Plasma Fup (%) | Healthy Adult: The Fup for the selected compound paired with a healthy adult physiology. The value can be edited if Scale Fup and Rbp is toggled On. Current Physiology / Fetal: The scaled Fup for the current compound-physiology pair, calculated based on the difference in plasma proteins. The value can’t be edited. |
Adjusted Plasma Fup (%) | Healthy Adult: The Experimental fup automatically adjusted by the program for possible binding to plasma lipids. This value cannot be edited. Current Physiology / Fetal: The scaled fup automatically adjusted by the program for possible binding to plasma lipids. This value cannot be edited. |
In-built GPX™ populations that show a difference in hematocrit and/or plasma proteins are: Pregnant, Pediatric, Cirrhosis CPA, CPB, and CPC and Renal Impairment (Mild, Moderate, Severe, and End Stage).
Therefore, activating the Scale Fup and Rbp toggle for these populations would be recommended.
Compartmental Panel
The Compartmental panel is used to enter parameters to define compartmental pharmacokinetic models for the selected compound. These compartmental models can be applied to any physiology available in the project by combining them in the Simulations view (see Compound Settings panel). Compartmental parameters that have been fitted and transferred using PKPlus™ (see PKPlus™ Module) are visible in this panel.
Pharmacokinetics view, Compartmental panel
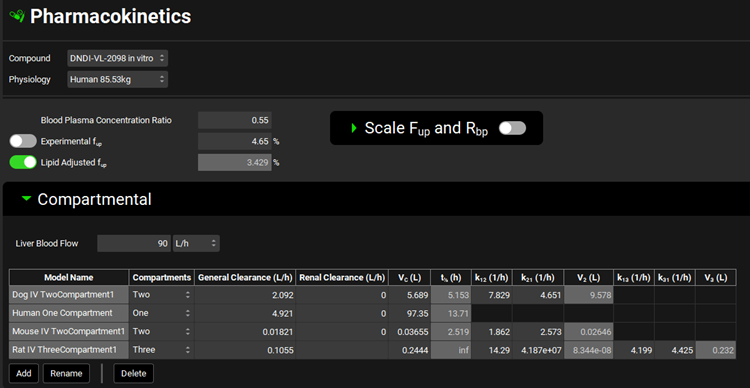
Input/Option | Description |
Liver Blood Flow | The liver blood flow used in the compartmental model, for the species selected above. This value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. This is a property of the physiology selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view and will be used in any simulations utilizing that physiology (see Drug Administration panel). |
Compartmental parameters table | Displays the available compartmental models and the associated parameters. Note: for parameters where normalizing by bodyweight is an option (General and Renal Clearance, Vc, V2 and V3), selecting the per kg option (by clicking on the units in the header and checking the white box) will normalize all values in that column by the bodyweight of the species selected above. Unchecking the box will recalculate the base values, also based on the bodyweight of the species selected above. |
Model Name | The name associated with the compartmental parameters in the given row. This name will be displayed for selection in the Simulation view (see Compound Settings panel). The name can be edited using the Rename button (see below). Compartmental models fitted in PKPlus™ and transferred here (See PKPlus™ Module) will be named automatically based on the PKPlus™ Run name and the number of compartments. |
Compartments | A drop-down. Selects the number of compartments to be used for the compartmental model (one, two or three). |
General Clearance | The clearance from the central compartment. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/h/kg, mL/min/kg, mL/s/kg) can be edited. See note above (Compartmental parameters table) when normalizing by bodyweight. |
Renal Clearance | The rate of renal clearance. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/h/kg, mL/min/kg, mL/s/kg) can be edited. See note above (Compartmental parameters table) when normalizing by bodyweight. This clearance is also from the central compartment and is separated from General Clearance to enable estimation of liver FPE. |
Vc | The volume of the central compartment. The value and the units (L, mL, L/kg, mL/kg) can be edited. See note above (Compartmental parameters table) when normalizing by bodyweight. For one-compartment drugs, this is the same as the total volume of distribution, Vd. For multi-compartment drugs, this is the central compartment volume, Vc. |
t½ | The terminal half-life calculated based on the other parameters entered. Neither the value nor the units may be edited. |
k12 / k21 / k13 / k31 | The micro-constants for distribution of drug to and from the second and third compartments, if used. The value and the units (1/h, 1/min) can be edited. |
V2 / V3 | The volumes for the second and third pharmacokinetic compartments, if used, calculated based on the micro-constants entered. The value cannot be edited but the units (L, mL, L/kg, mL/kg) can be edited. See note above (Compartmental parameters table) when normalizing by bodyweight. |
Add | Adds a compartmental model to the table - activates the Enter model name: input box to name the new model. |
Rename | Renames the currently selected compartmental model - activates the Enter the new model name: input box to rename the model. |
Delete | Deletes the currently selected compartmental model – Hold Ctrl-key and click to select the row containing the model for deletion. |
PBPKPlus™ panel
The PBPKPlus™ panel is used to enter parameters to define the physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for the selected compound and physiology. These PBPK models are applied automatically to a given simulation, when PBPK is selected as the Pharmacokinetics Model, based on the compound and physiology schedule set in the Simulations view (see Drug Administration panel).
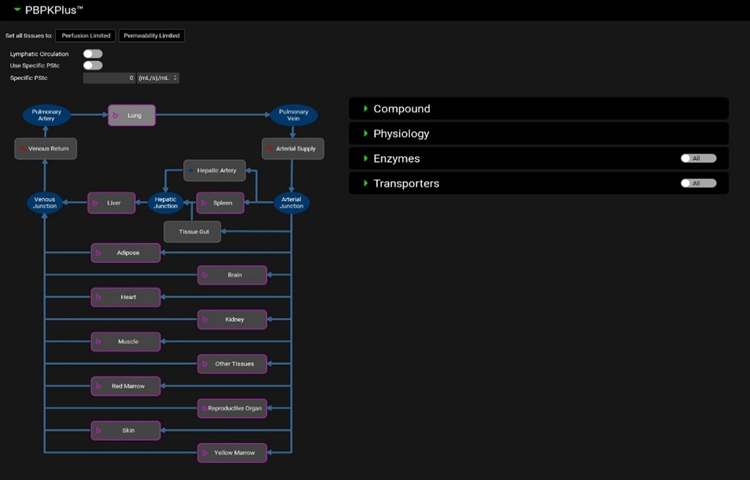
The panel consists of an interactive PBPK diagram, on the left-hand side of the interface, which shows the tissues in alphabetical order and the blood compartments that perfuse them. Each individual tissue and the grey (in Dark Theme) or white (in Light Theme) blood compartments can be selected by clicking on the icon. This displays detailed information on that tissue in the additional sub-panels on the right. The information displayed will be similar for most tissues, while Venous Return and Arterial supply have blood specific parameters. The exceptions to this are Hepatic Artery and Tissue Gut, which have blood flow as their only property. For Tissue Gut, this represents blood flow to (and from) the ACAT model described in detail on the Gastrointestinal Panel. The remaining blood compartments (Pulmonary Artery, Pulmonary Vein, Arterial Junction, Hepatic Junction, and Venous Junction) cannot be selected, as these are for illustrative purposes only, and do not have individual properties.
Under the interactive diagram is the PBPK model table. Further sub-panels below the table contain the options available to calculate the Kps. The calculated volume of distribution at steady state, systemic clearance and derived half-life are displayed at the bottom of the table.
Additional entries will be present for pregnant physiologies.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Interactive PBPK diagram and associated sub-panels, with Lung selected
Input/Option | Description |
Set all tissues to: | Two buttons that will change all tissues in the model to Perfusion Limited or Permeability Limited, respectively. |
Lymphatic Circulation | A toggle. Turned off by default. Turn on (the toggle will go green) to include the lymphatic circulation in the PBPK model. This setting should be activated for small molecules if this process contributes significantly to the drug’s disposition. |
Use Specific PStc | A toggle. Turned off by default. Turn on to use the Specific PStc, together with the total cell volume of each tissue, to calculate the PStc for any permeability limited tissues in the model. |
Specific PStc | The value, in (mL/s)/mL, of the Specific PStc. The value can be edited. |
Pregnant Physiologies
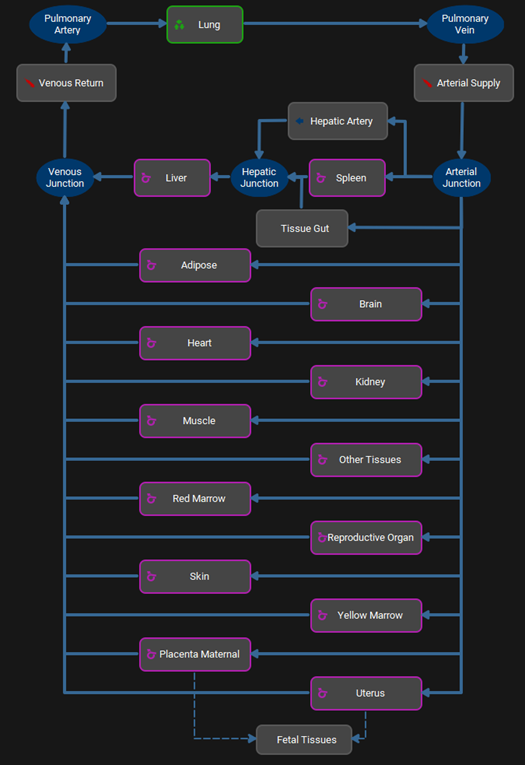
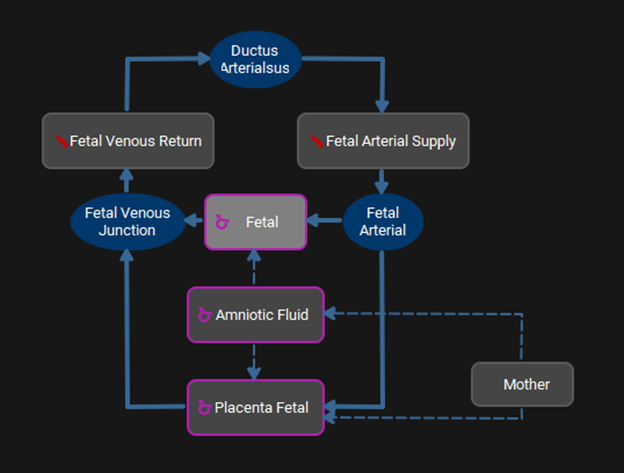
Additional tissues are visible in the interactive PBPK diagram and the properties of the Placenta Maternal and Uterus can be viewed in the sub-panels as for the other tissues. To access the interactive PBPK diagram for the fetus, double click on Fetal Tissues. To return to the main interactive PBPK diagram double click on Mother. The fetal diagram behaves identically to the main diagram described above.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, PBPK diagram for a pregnant physiology
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, PBPK diagram for the physiology of the fetus
Add & Remove Tissues
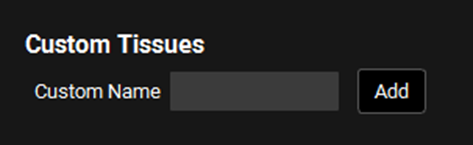
GastroPlus® supports the addition of custom tissues to the PBPK model, as well as the deletion of default built-in tissues. Custom tissues possess the same properties (volume, perfusion, composition, etc.) as the default tissues, the values for which must be defined by the user after the custom tissue is added. All custom tissues are connected to Arterial Supply and Venous Return, and cannot have an apical side. Intrinsic clearance, enzyme expression, and basolateral transporters (if the tissue type is permeability limited) are also supported for custom tissues.
There is no limit to the number of custom tissues that can be added. Of the built-in tissues, the following are required and cannot be deleted: Arterial Supply, Hepatic Artery, Venous Return, Liver, Lung, Spleen, and Tissue Gut.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Custom tissues section
Input/Option | Description |
Custom Name | The name of the custom tissue. Type the desired name in the input field and click “Add”. The added custom tissue will show up at the bottom of the PBPK diagram. |
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, PBPK diagram, Yellow Marrow tissue Right-Click Menu
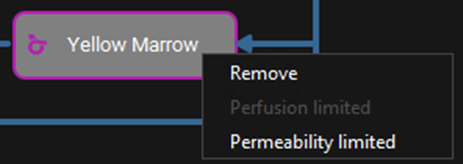
Input/Option | Description |
Remove | Deletes the tissue selected in the PBPK model. |
Perfusion limited | Changes the tissue model to Perfusion Limited |
Permeability limited | Changes the tissue model to Permeability Limited |
Compound sub-panel - Tissues
The Compound sub-panel contains information on compound properties in the selected tissue. These properties are linked to the compound-physiology pair selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view.
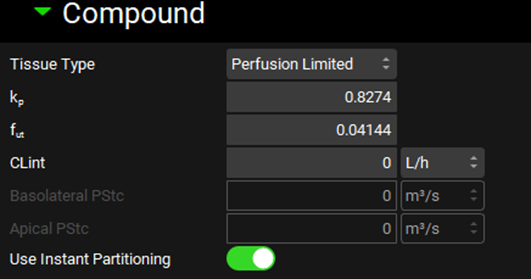
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Compound sub-panel, Perfusion limited tissue
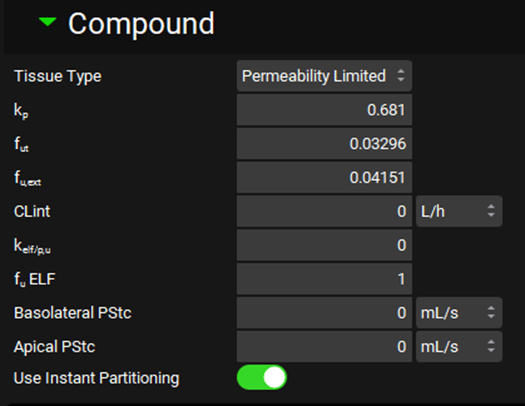
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Compound sub-panel, Permeability limited tissue (with Lung selected in the interactive PBPK diagram)
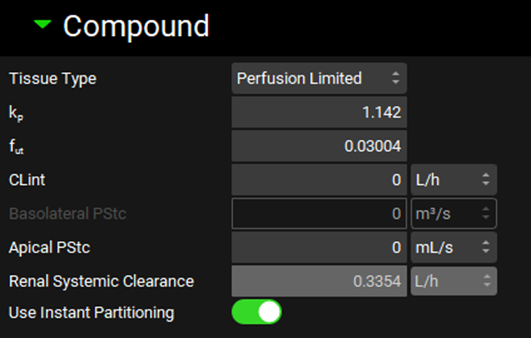
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Compound sub-panel (with Kidney selected in the interactive PBPK diagram)
Input/Option | Description |
Tissue Type | A drop-down. Selects whether the individual tissue is perfusion or permeability limited. This selection may also be changed by right clicking on the tissue in the interactive diagram or from the Tissue Type drop-down in the PBPK table (see below). Perfusion Limited tissues have a purple border in the interactive diagram, whilst the border of Permeability Limited tissues is green. |
kp | The tissue to plasma partition coefficient (kp) for the selected tissue. This value can be edited. For perfusion limited tissues this determines the concentration of drug in the tissue. For permeability limited tissues this determines the concentration of drug in the extracellular compartment. |
fut | The fraction unbound in the tissue for a perfusion limited tissue, or the fraction unbound in the intracellular compartment for a permeability limited tissue. These values can be edited. |
fu,ext | The fraction unbound in the extracellular compartment for a permeability limited tissue. Only active when the selected tissue is permeability limited. This value can be edited. |
CLint | The unbound intrinsic clearance for the selected tissue. The value and the units can be edited (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min). If the value is edited here, the PBPK table automatically updates (see below) |
Kelf/p,u | The epithelial lining fluid (ELF) / unbound plasma partition coefficient. Active for lung only. Used to calculate the amount of drug in the ELF assuming instant partitioning when the lung is perfusion limited. The value can be edited. |
fu ELF | The fraction unbound in the epithelial lining fluid. Active for lung only. This value can be edited. |
Basolateral PStc | Basolateral Permeability-Surface Area product for passive diffusion between extracellular and intracellular compartments. Active when a tissue is permeability limited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled Off, the value and the units (mL/s, L/h) can be edited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled On, this value is calculated based on specific PStc and cannot be edited. |
Apical PStc | Apical Permeability-Surface Area product for passive diffusion between tissue or intracellular compartment and ELF, kidney tubules or bile for the lung, kidney and liver, respectively. Used to calculate the amount of drug in the ELF assuming slow diffusion. Active for lung, liver and kidney whether the tissue is perfusion limited or permeability limited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled Off, the value and the units (mL/s, L/h) can be edited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled On, this value is calculated based on specific PStc and cannot be edited, with the exception of liver. |
Renal Systemic Clearance | The systemic renal clearance. The value is calculated based on the filtration clearance, the intrinsic clearance and the clearance due to passive secretion and reabsorption (where applicable). The units can be edited (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min). Visible for kidney and fetal tissues only. |
Use Instant Partitioning | A toggle. On by default. Turning it off for one tissue turns it off for all tissues. |
Compound sub-panel – Blood Compartments
The Compound sub-panel is active only for Venous Return, Arterial Supply, Fetal Venous Return and Fetal Arterial Supply and simply displays the intrinsic clearance for that compartment. The intrinsic clearance value is shared between Venous Return and Arterial Supply, editing the clearance value for one will automatically update the other.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Compound sub-panel, Blood Compartment
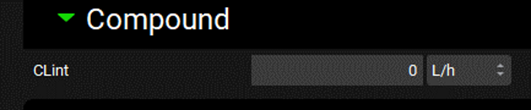
Input/Option | Description |
CLint | The unbound intrinsic clearance for the selected compartment. The value and the units can be edited (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min). If the value is edited here, the PBPK table automatically updates (see below). Active for Venous Return, Arterial Supply, Fetal Venous Return and Fetal Arterial Supply. |
Physiology sub-panel - Tissues
The Physiology sub-panel contains information about physiological parameters for the selected tissue. These properties are linked to the physiology selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Physiology sub-panel for the Lung
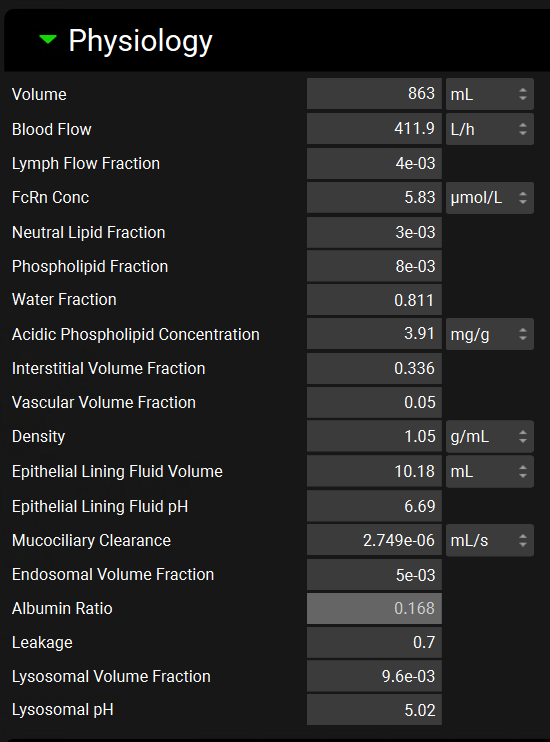
Input/Option | Description |
Volume | The total volume of the selected tissue. The value and the units (mL, L) can be edited. |
Blood Flow | The blood flow of the selected tissue. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. |
Lymph Flow Fraction | The lymphatic flow of the selected tissue as a percentage of plasma flow. The value can be edited. |
FcRn Conc | The concentration of neonatal Fc receptor in the selected tissue in umol/L. The value can be edited. |
Neutral Lipid Fraction | The neutral lipid content of the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the wet tissue weight. The value can be edited. |
Phospholipid Fraction | The phospholipid content of the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the wet tissue weight. The value can be edited. |
Water Fraction | The water content of the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the wet tissue weight. The value can be edited. |
Acidic Phospholipid Fraction | The concentration of acidic phospholipids in the selected tissue. The value and the units (mg/g, g/g) can be edited. |
Interstitial Volume Fraction | The volume of the interstitial space for the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the total tissue volume. The value can be edited. |
Vascular Volume Fraction | The volume of the vascular space for the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the total tissue volume. The value can be edited. |
Density | The tissue density for the selected tissue. The value and the units (g/mL, mg/L, mg/mL) can be edited. |
Epithelial Lining Fluid Volume | Visible for lung only. The volume of the epithelial lining fluid in the lung. The value and the units (mL, L) can be edited. |
Epithelial Lining Fluid pH | Visible for lung only. The pH of the epithelial lining fluid in the lung. The value can be edited. |
Mucociliary Clearance | Visible for lung only. The mucociliary clearance rate in the lung. The value and the units (mL/s, mL/min, L/h, L/min) can be edited. |
Endosomal Volume Fraction | The volume of the endosomal space for the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the total tissue volume. The value can be edited. |
Albumin Ratio | The albumin tissue to plasma concentration ratio for the selected tissue. This is set as specified in the Tissue Albumin drop-down in the Advanced Options sub-panel (see Advanced Options sub-panel below). |
Leakage | The level of leakage from the vasculature of the selected tissue using muscle as a reference (=1). A value <1 indicates a leaky tissue, a value >1 indicates a tight tissue. The value can be edited. |
Lysosomal Volume Fraction | The volume of the lysosomes for the selected tissue expressed as a fraction of the total tissue volume. The value can be edited. |
Lysosomal pH | The pH of the lysosomes in the selected tissue. The value can be edited. |
Additional inputs for Fetal Tissues
Input/Option | Description |
Swallowing Rate | The fetal swallowing rate. The value and the units (mL/s, mL/d, mL/min, L/h, L/min) can be edited. Relevant for Amniotic Fluid only. |
Secretion Rate | The secretion rate from the fetal tissue. The value and the units (mL/s, mL/d, mL/min, L/h, L/min) can be edited. Relevant for Amniotic Fluid only. |
Transmembraneous Rate | The transport rate between the amniotic fluid and uterus wall. The value and the units (mL/s, mL/d, mL/min, L/h, L/min) can be edited. Relevant for Amniotic Fluid only. |
Intramembraneous Osmotic Rate | The passive transport rate of the solute and water between the amniotic fluid and fetal blood which occurs in placenta, fetal skin and umbilical cord. Related to osmolarity. The value and the units (mL/s, mL/d, mL/min, L/h, L/min) can be edited. Relevant for Amniotic Fluid only. |
Intramembraneous Vesicular Rate | The active transport rate of the solute and water between the amniotic fluid and fetal blood which occurs in placenta, fetal skin and umbilical cord. Driven by vesicular pressure. The value and the units (mL/s, mL/d, mL/min, L/h, L/min) can be edited. Relevant for Amniotic Fluid only. |
Placental Villi Area | The surface area of the placental villi in m2. The value can be edited. Relevant for Placental Fetal only. |
Physiology sub-panel – Blood Compartments
The Physiology sub-panel contains information about physiological parameters for the selected blood compartment. These properties are linked to the physiology selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view. Other than volume, all properties are shared between Venous Return and Arterial Supply (and between Fetal Venous Return and Fetal Arterial Supply) and editing a parameter for one will automatically update the other.
The majority of the parameters do not apply to the Hepatic Artery or Tissue Gut, with the exception of Blood Flow.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Physiology sub-panel for Venous Return
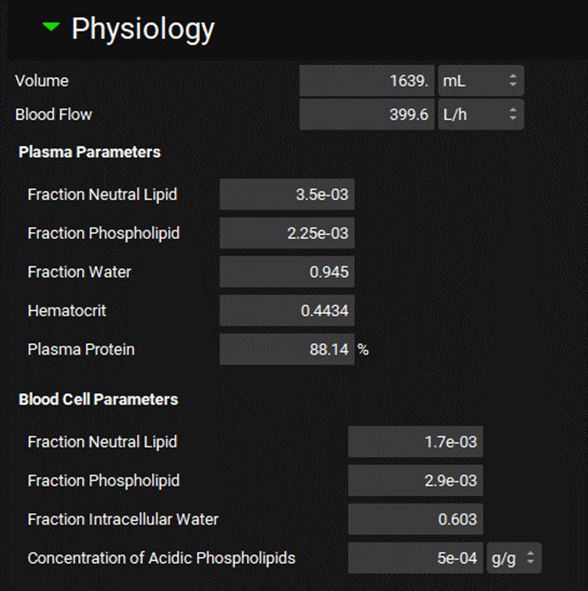
Input/Option | Description |
Volume | The total volume of the selected compartment. The value and the units (mL, L) can be edited. |
Blood Flow | The blood flow of the selected compartment. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. This is the only parameter in this table that applies to Hepatic Artery and Tissue Gut. |
Plasma Parameters | The following parameters all apply to plasma fraction of the compartment. |
Fraction Neutral Lipid | The neutral lipid content of plasma. The value can be edited. |
Fraction Phospholipid | The phospholipid content of plasma. The value can be edited. |
Fraction Water | The water content of plasma. The value can be edited. |
Hematocrit | The hematocrit. The value can be edited. |
Plasma Protein | The total plasma protein expressed as a percentage of the typical adult amount. The value can be edited. |
Blood Cell Parameters | The following parameters all apply to the blood cell fraction of the compartment. |
Fraction Neutral Lipid | The neutral lipid content of red blood cells. The value can be edited. |
Fraction Phospholipid | The phospholipid content of red blood cells. The value can be edited. |
Fraction Intracellular Water | The intracellular water content of red blood cells. The value can be edited. Note: the extracellular water content is equal to 0. |
Concentration of Acidic Phospholipids | The concentration of acidic phospholipids in red blood cells in grams per gram of tissue. The value can be edited. |
Urine sub-panel - Tissues
The Urine sub-panel contains information about physiological parameters for the selected tissue and is active for Kidney and Fetal tissues.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Urine sub-panel (only visible if Kidney or Fetal is selected in the interactive PBPK diagram)
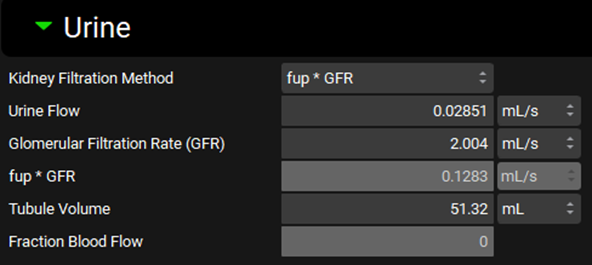
Input/Option | Description |
Kidney Filtration Method | A drop-down. Selects the method used to calculate the filtration clearance: fup * GFR (the unbound glomerular filtration rate), Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), Fraction Blood Flow, or User Specified. The method selected determines which of the following parameters are visible. |
Urine Flow | The urine flow rate. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. |
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) | The glomerular filtration rate. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. This value is used as the filtration clearance when Glomerular Filtration is selected as the Kidney Filtration Method. |
fup * GFR | The calculated unbound glomerular filtration rate (mL/s). Calculated by multiplying the experimental fraction unbound in the plasma for the selected compound in the selected physiology by the GFR determined above. Neither the value nor the units can be edited. Note that this calculation always uses Experimental fup, not Lipid Adjusted fup, regardless of the selection in the general settings. Visible when fup * GFR is selected as the Kidney Filtration Method. |
Tubule Volume | The volume of the kidney tubules. The value and the units (mL, L) can be edited. |
User Defined Filtration Clearance | The filtration clearance (L/h). The value can be edited and is then used as entered to determine the filtration clearance when the Kidney Filtration Method is set to User Defined. Setting this value to 0 will effectively disable renal filtration clearance. Visible when User Defined is selected as the Kidney Filtration Method. |
Calculated Filtration Clearance | The calculated filtration clearance (mL/s). Calculated by multiplying kidney blood flow, as defined in the Physiology sub-panel above, by the Fraction of Blood Flow. Neither the value nor the units can be edited. Visible when Fraction Blood Flow is selected as the Kidney Filtration Method. |
Fraction of Blood Flow | The fraction of kidney blood flow to be used to calculate the filtration clearance. This value can be edited when Fraction Blood Flow is selected as the Kidney Filtration Method. |
Enzymes sub-panel – Tissues and Blood Compartments
The Enzymes sub-panel displays information on enzymes expressed in the selected tissue, for the physiology selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view. Enzymes can be filtered based on those assigned to the compound (See Enzyme Kinetics panel) selected at the top of the view using the All/Active Toggle.
Enzymes cannot be added to Hepatic Artery, Fetal Venous Return or Fetal Arterial Supply. Enzymes added to either Arterial Supply or Venous Return will be automatically added to the other.
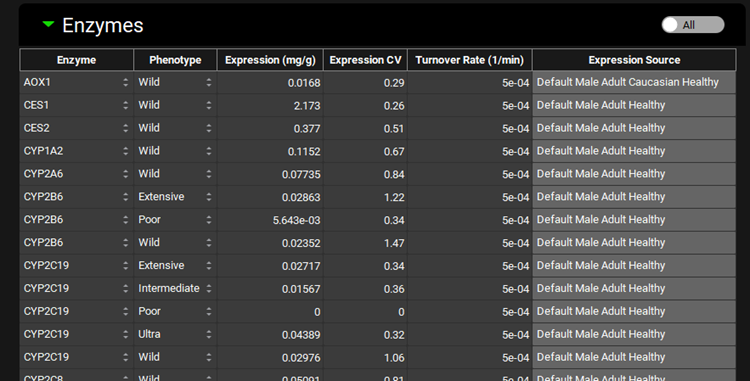
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Enzymes sub-panel (Liver, All Enzymes, Partial Screenshot)
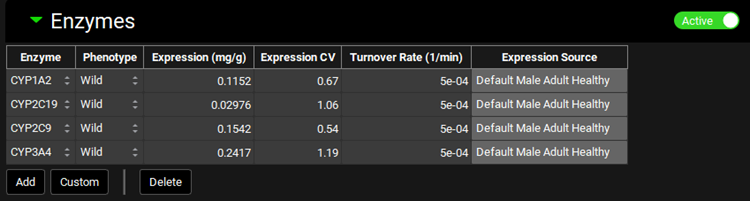
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Enzymes sub-panel (Liver, Active Enzymes)
Input/Option | Description |
Enzyme | Indicates the enzyme for which expression information is shown. Different enzymes may be selected using the drop-down. |
Phenotype | The phenotype of the indicated enzyme. A different phenotype may be selected using the drop-down (Wild, Poor, Intermediate, Extensive, Ultra) however, for enzymes where the change in Expression is not available it will need to be updated manually. |
Expression | The expression of the enzyme in the selected tissue. This value, multiplied by the tissue mass, is then multiplied by the PBPK Vmax in the Enzyme Kinetics table to get the final Vmax used in the simulation. The value and the units (mg enzyme/g tissue, µg/g, mg/kg, µg/kg) can be edited. |
Expression CV | The covariance of the expression for the indicated enzyme in the selected tissue. The value can be edited. |
Turnover Rate | The turnover rate of the indicated enzyme in the selected tissue. The value and the units (1/min, 1/h, 1/s) can be edited. |
Expression Source | The source of the expression levels of the indicated enzyme in the selected tissue. Values that have been edited from the default, or custom enzymes, will have a source of User-Defined. Otherwise, the source will reflect the physiology the expression was derived from. |
All/Active | A toggle. Controls whether the enzymes shown will be filtered based on the compound selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view. |
Add | Add an enzyme entry for the species of the current physiology. Once the enzyme is created, it will be added automatically as a row to the table. Enzymes added here must still be assigned to the intended compound using the Enzyme Kinetics table on the Compounds view. |
Custom | Add a custom enzyme for the species of the current physiology. Once the custom enzyme is created, it will be added automatically as a row to the table. It will also be available thereafter in the enzyme drop-down for selection. Custom enzymes added here must still be assigned to the intended compound using the Enzyme Kinetics table on the Compounds view. |
Delete | Delete the selected row from the table. Hold Ctrl-key and click anywhere in the row to select the row for deletion. |
When adding or changing enzymes, the table will automatically sort alphabetically based on enzyme name. If the filter is set to Active, the enzyme also needs to be assigned to the compound in the Enzyme Kinetics table in the Compounds view before it will show up in this table.
Where units can be edited, this is done by clicking in the column header.
Transporters sub-panel – Tissues and Blood Compartments
The Transporters sub-panel displays information on transporters expressed in the selected tissue, for the physiology selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view. Transporters can be filtered based on those assigned to the compound (See Transporter Kinetics panel) selected at the top of the view using the All/Active Toggle.
Transporters cannot be added to Hepatic Artery, Venous Return, Arterial Supply, Fetal Venous Return, or Fetal Arterial Supply.
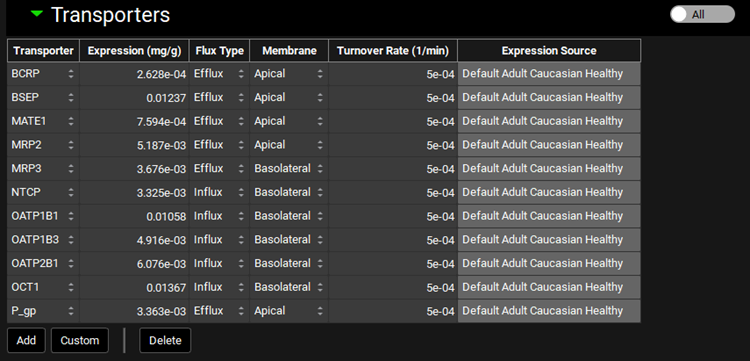
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Transporter sub-panel, (Liver, All Transporters)
Input/Option | Description |
Transporter | Indicates the transporter for which expression information is shown. Different transporters may be selected using the drop-down. |
Expression | The expression of the transporter in the selected tissue. This value, multiplied by the tissue mass, is then multiplied by the PBPK Vmax in the Transporter Kinetics table to get the final Vmax used in the simulation. The value and the units (mg transporter/g tissue, µg/g, mg/kg, µg/kg) can be edited. |
Flux Type | Indicates the flux direction (influx or efflux) for the transporter. Flux type may be changed using the drop-down. |
Membrane | Indicates the membrane location (apical or basolateral) for the transporter. Membrane location may be changed using the drop-down. |
Turnover Rate | The turnover rate, of the indicated transporter in the selected tissue. The value and the units (1/min, 1/h, 1/s) can be edited. |
Expression Source | The source of the expression levels of the indicated transporter in the selected tissue. Values that have been edited from the default, or custom transporters, will have a source of User-Defined. Otherwise, the source will reflect the physiology the expression was derived from. |
All/Active | A toggle. Controls whether the transporters shown will be filtered based on the compound selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view. |
Add | Add a transporter entry for the species of the current physiology. Once the transporter is created, it will be added automatically as a row to the table. Transporters added here must still be assigned to the intended compound using the Transporter Kinetics table on the Compounds view. |
Custom | Add a custom transporter for the species of the current physiology. Once the custom transporter is created, it will be added automatically as a row to the table. It will also be available thereafter in the transporter drop-down for selection. Custom transporters added here must still be assigned to the intended compound using the Transporter Kinetics table on the Compounds view. |
Delete | Delete the selected row from the table. Hold Ctrl-key and click anywhere in the row to select the row prior to deletion. |
Where units can be edited, this is done by clicking in the column header.
PBPK Table
The PBPK table contains a summary of all parameters for each tissue. All information within is linked to the physiology and the compound selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view. For pregnant physiologies, Fetal, Placenta Fetal, Placenta Maternal and Uterus will be added to the PBPK table.
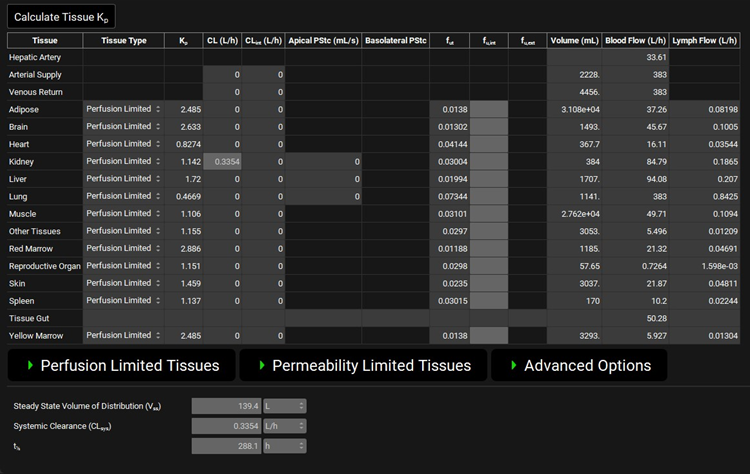
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, PBPK table
Input/Option | Description |
Calculate Tissue Kp | A button. Clicking causes the Kp for each tissue to be recalculated using the methods selected in the sub-panels (see below) and the compound inputs. Note: The Kps will not be recalculated based on theoretical values if User Defined is selected as the Kp calculation method (see below). |
Tissue | Identifies the tissue or circulatory compartment to which all other information in the row applies. The tissues are listed in alphabetical order. |
Tissue Type | A drop-down. Selects whether the individual tissue is perfusion or permeability limited. |
Kp | The partition coefficient (kp) for the selected tissue. This value can be edited. For perfusion limited tissues this determines the concentration of drug in the tissue. For permeability limited tissues this determines the concentration of drug in the extracellular compartment. |
CL | The systemic plasma clearance of the compound in the specified tissue. Calculated from the CLint (see below). The value and the units can be edited (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min). Editing the value causes a recalculation of the CLint so the two values remain aligned. Note: assigning a CL in one circulatory compartment (arterial supply or venous return) will automatically enter the same clearance in the other circulatory compartment. |
CLint | The unbound intrinsic clearance. The value and the units can be edited (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min). Editing the value causes a recalculation of the CL so the two values remain aligned. Note: assigning a CLint in one circulatory compartment (arterial supply or venous return) will automatically enter the same clearance in the other circulatory compartment. |
Apical PStc | Apical Permeability-Surface Area product for passive diffusion between tissue or intracellular compartment and ELF, kidney tubules or bile for the lung, kidney, and liver, respectively. Used to calculate the amount of drug in the ELF assuming slow diffusion. Active for lung, liver and kidney whether the tissue is perfusion limited or permeability limited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled Off, the value and the units (mL/s, L/h) can be edited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled On, this value is calculated based on specific PStc and cannot be edited, with the exception of liver. |
Basolateral PStc | Basolateral Permeability-Surface Area product for passive diffusion between extracellular and intracellular compartments. Active when a tissue is permeability limited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled Off, the value and the units (mL/s, L/h) can be edited. If Use Specific PStc is toggled On, this value is calculated based on specific PStc and cannot be edited. |
fut | The fraction unbound in the tissue for a perfusion limited tissue. These values can be edited. |
fu,int | The fraction unbound in the intracellular compartment for a permeability limited tissue. Only active when the selected tissue is permeability limited. This value can be edited. |
fu,ext | The fraction unbound in the extracellular compartment for a permeability limited tissue. Only active when the selected tissue is permeability limited. This value can be edited. |
Volume | The volume of the indicated tissue. The value and the units (mL, L) can be edited. |
Blood Flow | The blood flow of the selected tissue. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. |
Lymph Flow | The lymphatic flow of the selected tissue. The value and the units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited. |
Updates to the PBPK table are reflected in the sub-panels linked to the interactive PBPK diagram.
Note: Where units can be edited, this is done by clicking in the column header.
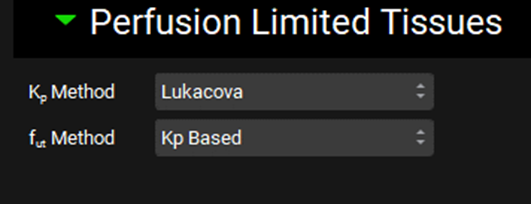
Perfusion Limited Tissues sub-panel
The Perfusion Limited Tissues sub-panel is where the calculation methods to be used for the calculation of the partition coefficient and the fraction unbound for perfusion limited tissues are selected. These properties are linked to the compound-physiology pair selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Perfusion Limited Tissues sub-panel
Input/Option | Description |
Kp Method | A drop-down. Selects the method used to calculate the partition coefficient (kp) for perfusion limited tissues. The following methods are available:
If User Defined is selected, the Calculate Tissue Kp button will not work. |
fut Method | A drop-down. Selects the method used to calculate the fraction unbound in the tissue for perfusion limited tissues. The following methods are available:
|
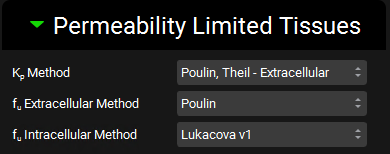
Permeability Limited Tissues sub-panel
The Permeability Limited Tissues sub-panel is where the calculation methods to be used for the calculation of the partition coefficient and the extracellular and intracellular fractions unbound for permeability limited tissues are selected. These properties are linked to the compound-physiology pair selected at the top of the Pharmacokinetics view.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Permeability Limited Tissues sub-panel
Input/Option | Description |
Kp Method | A drop-down. Selects the method used to calculate the partition coefficient (kp) for permeability limited tissues. The following methods are available:
If User Defined is selected, the Calculate Tissue Kp button will not work. |
fu Extracellular Method | A drop-down. Selects the method used to calculate the fraction unbound in the extracellular compartment for permeability limited tissues. The following methods are available:
|
fu Intracellular Method | A drop-down. Selects the method used to calculate the fraction unbound in the intracellular compartment for permeability limited tissues. The following methods are available:
|
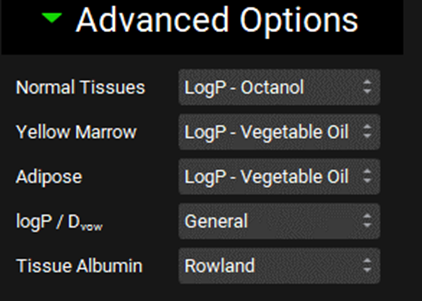
Advanced Options sub-panel
The Advanced Options sub-panel allows for specific modifications of the selected Kp calculation method.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Perfusion Limited Tissues sub-panel
Input/Option | Description |
Normal Tissues | A drop-down. Selects the lipophilicity used in the Kp calculation for all tissues that are not defined as adipose (see Physiology sub-panel - Tissues). The following methods are available:
|
Yellow Marrow | A drop-down. Selects the lipophilicity used in the Kp calculation for Yellow Marrow. The following methods are available:
|
Adipose | A drop-down. Selects the lipophilicity used in the Kp calculation for all tissues that are defined as adipose (see Physiology sub-panel - Tissues). The following methods are available:
|
LogP / Dvow | A drop-down. Selects the equation to use to convert the octanol/water partition coefficient to the vegetable oil/water partition coefficient. Vegetable oil/water distribution coefficient is then calculated by taking into consideration drug’s ionization. The following methods are available:
Note: General is the equation published by Poulin 1 2 , Base is recommended for bases with pKa > 7 and logP > 2. |
Tissue Albumin | A drop-down. Selects the albumin tissue:plasma concentration ratio values. The following methods are available:
|
Please see below for the mapping of calculation method names between GPX™ and Legacy GastroPlus®.
| GPX™ | Legacy GastroPlus® |
Kp Method | Poulin, Theil – Homogeneous | Poulin, Theil – Homogeneous |
Poulin, Theil – Extracellular | Poulin, Theil – Extracellular | |
Berezhkovskiy | Berezhkovskiy | |
Rodgers, Leahy, Rowland | Rodgers, Leahy, Rowland | |
Lukacova | Lukacova (Rodgers-Single) | |
Lukacova with Lysosomes | Lukacova with Lysosomes | |
User Defined | User Defined | |
Fut (Perfusion Limited) | Poulin | Poulin Eq. |
Lukacova v1 | S+ v9.0 and earlier | |
Kp Based | S+ v9.5 (Default) | |
Fu extracellular (Permeability Limited) | Poulin | Poulin Eq. |
Kp Based | S+ v9.5 (Default) | |
Fu intracellular (Permeability Limited) | Poulin | Poulin Eq. |
Lukacova v1 | S+ v9.0 and earlier | |
Lukacova v2 with lysosomes | S+ v9.5 w/Lys | |
Lukacova v2 | S+ v9.5 (Default) |
Input/Option | Description |
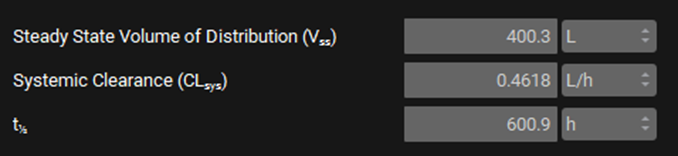
Steady State Volume of Distribution (Vss) | Estimated volume of distribution at steady state based on the settings selected for the PBPK model. The units (L, mL) can be edited using the drop-down. |
Systemic Clearance (CLsys) | Calculated systemic plasma clearance based on the sum of the systemic plasma clearance in each tissue. The units (L/h, mL/min, mL/s, L/min) can be edited using the drop-down. Note that metabolic clearance and transporter-based elimination, as set up via the enzyme and transporter kinetics for the selected compound, will not be counted in this number. |
t½ | The calculated half-life based on the Vss and CLsys determined above. |
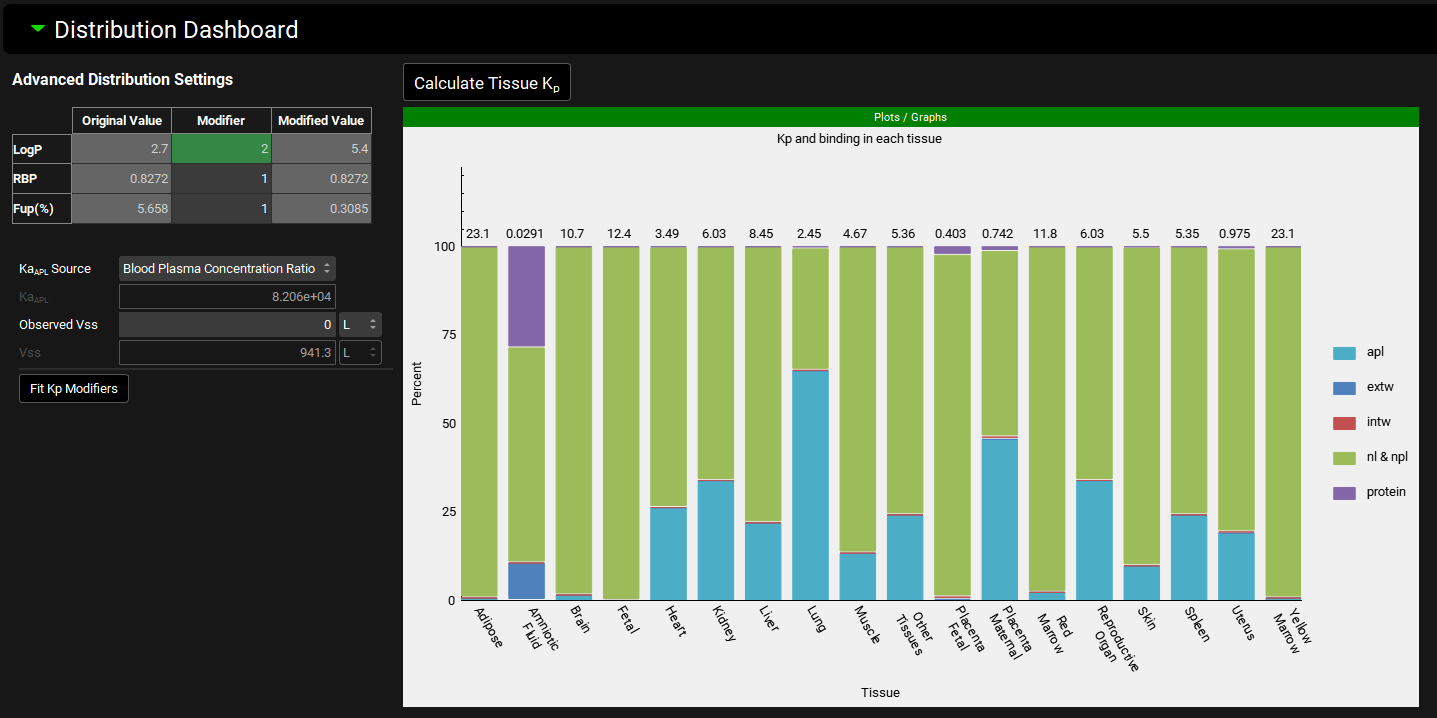
Distribution Dashboard
The Distribution Dashboard provides detailed information about mechanistic tissue distribution and control over advanced distribution settings. The advanced distribution settings are comprised of the Kp Modifiers, including the ability to fit these modifiers to an Observed Steady State Volume of Distribution (Vss), and the selection of the acidic phospholipid binding constant (KaAPL) source, including the ability to calculate it from a measured tissue Kp. The sub-panel also includes a plot showing how the selected compound binds to or partitions into each tissue component, based on the currently selected Kp calculation method.
Kp Modifiers
The Kp Modifiers are multipliers that can be used to mechanistically scale drug distribution. They are provided for LogP/LogD, Blood to Plasma Concentration Ratio (RBP), and Fraction Unbound in Plasma (Fup, as %), which are three key properties used in the calculation of Kp values. The modified value is used in the calculation of Kps only, and does not impact other calculations using these properties, such as intrinsic clearance or renal filtration via fup * GFR. They do not directly impact the calculation of fraction unbound in tissue; however, if the fut method is set to Kp Based, then the modifiers will indirectly impact the fut calculations. Of note, the Fup modifier acts on the experimental fup, prior to the calculation of the Lipid Adjusted fup. It is also important to note that because LogD is used in the calculation of Lipid Adjusted fup, changing the LogD modifier will also modify the Lipid Adjusted fup in the context of Kp calculations.
Vss Fitting
The Distribution Dashboard also provides the option to fit the Kp Modifiers to an Observed Steady State Volume of Distribution (Observed Vss). Each modifier will be fitted independently within physiologically valid ranges, and the best modifier will be selected and automatically applied. The criteria for selection are based on both minimizing the error between predicted and observed Vss, and minimizing the change from baseline of the Kp Modifier.
As such, only one Kp Modifier will ever be visibly updated when using the “Fit Kp Modifiers” function on the Distribution Dashboard, even though all three are tested in the background. Furthermore, there is a floor to the predicted Vss, based on the volume of plasma and extracellular fluid, so there may be rare cases when an observed Vss is below this value, and a perfect fit is not attainable. Lastly, the predicted Vss may not accurately capture time-dependent distribution, and as such has limited utility when a significant portion of the body is represented by permeability-limited tissues.
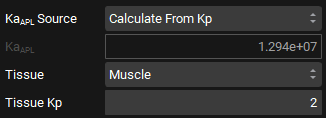
KaAPL Calculations
The KaAPL Source allows additional control over the calculation of the binding of the compound to acidic phospholipids. The default source is Blood Plasma Concentration ratio, which estimates the association constant from RBP (see Scientific Principles Guide). The calculation of KaAPL from RBP is affected by the RBP modifier.
If measured tissue Kp values are available, the KaAPL can be back calculated from the measured Kp using the currently selected Kp method for the indicated tissue, and the calculated KaAPL will then be applied to all tissues when calculating Kps. Note that this only applies for Kp calculation methods that utilize KaAPL, namely Lukacova and Lukacova with Lysosomes for compounds with any basic or mixed pKa, and Rodgers, Leahy, Rowland for strong bases.
Lastly, a User Defined option is available for manual entry of a KaAPL value.
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Distribution Dashboard sub-panel
Pharmacokinetics view, PBPKPlus™ panel, Distribution Dashboard sub-panel, with KaAPL source set to Calculate from Kp
Input/Option | Description |
Kp Modifier Table | A table for each Kp modifier showing the original value, the current modifier, and the modified value. The modified value is what is used in the Kp calculations. The modified value may be capped based on physiological constraints.
|
KaAPL Source | A drop-down. Selects the source of the acidic phospholipid binding constant (KaAPL). Options include:
|
KaAPL | Displays the current KaAPL value. If the KaAPL Source is set to Blood Plasma Concentration Ratio or Calculate from Kp, this field will be read only and display the calculated value. If the KaAPL Source is set to User Defined, the desired value can be typed in this field. Note that KaAPL is only relevant for molecules with a basic pKa using the Lukacova, Lukacova with Lysosomes, or Rodgers, Leahy, Rowland Kp calculation methods. |
Tissue | A drop-down. Selects which tissue to use when calculating KaAPL from a measured tissue Kp. Applicable only when KaAPL Source is set to Calculate From Kp. |
Tissue Kp | Number entry field for the experimentally measured tissue Kp. Applicable only when KaAPL Source is set to Calculate From Kp. |
Observed Vss | Number entry field for the experimentally Observed Steady State Volume of Distribution (Vss). The value can be edited. |
Vss | Displays the predicted Vss in L. |
Fit Kp Modifiers | A button. Automatically fits the best Kp Modifiers to match the entered Observed Vss. The modifier with the combined lowest error in Vss prediction and lowest change from baseline is automatically selected. |
Calculate Tissue Kp | A button. Recalculates tissue partition coefficients (Kps) for the PBPK model. This serves the same function as the Calculate Tissue Kp button in the main PBPKPlus™ panel. |
Tissue Distribution Plot | A stacked bar chart showing tissue-specific Kp values and the percentage of drug binding/partitioning to each tissue component. The specific components shown will depend on both the compound properties and the Kp calculation method selection. Note that when the Kp method is set to User Defined, the corresponding tissues will not be present in the plot. Note that this plot updates in real-time when the Kp modifiers and/or the KaAPL Source or value are changed, providing a preview of any adjustments in the advanced distribution settings. However, these changes will not be reflected in the model as a whole until the Calculate Tissue Kp button is clicked. |
- Poulin, P. and Theil, F.P. (2002). “Prediction of pharmacokinetics prior to in vivo studies. 1. Mechanism-based prediction of volume of distribution.” J. Pharm. Sci. 91(1): 129-56.
- Poulin, P. and Theil, F.P. (2002). “Prediction of pharmacokinetics prior to in vivo studies. II. Generic physiologically based pharmacokinetic models of drug disposition.” J. Pharm. Sci. 91(5): 1358-70.
- Rodgers T. and Rowland M. (2006). “Physiologically-based Pharmacokinetic Modeling 2: Predicting the tissue distribution of acids, very weak bases, neutrals and zwitterions.” J. Pharm. Sci. 95(6):1238-57.
- Rothschild, M.A., Bauman, A., et al. (1955). “Tissue distribution of I131 labeled human serum albumin following intravenous administration.” J. Clin. Invest. 34(9): 1354-8.
