Physiologies View
The Physiologies View has six panels. All the inputs and options on these for panels (and where applicable, their sub-panels) are described below. See:
Physiologies view
Input/Option | Description |
Compound | A drop-down. Selects the current compound. Options are populated based on compounds already added to the project. If no compounds have been added, this will be blank. If no compound is selected, once a physiology has been created, only the Characteristics panel will be enabled. |
Physiology | A drop-down. Selects the current physiology, populated based on physiologies added to the project. If no physiologies have been added, this will be blank. A physiology must be selected to enable all panels below.
Note that any existing physiomolecular properties will be copied with the physiology (See Physiomolecular Properties Selection Pop up).
|
Characteristics Panel
The Characteristics panel is used to enter demographic and related information for the selected physiology, such as species, weight, and age. This information determines all physiological features of the subject, including calculation of PEAR parameters for PBPK models. Of note, physiological parameters will be recalculated when characteristics are changed.
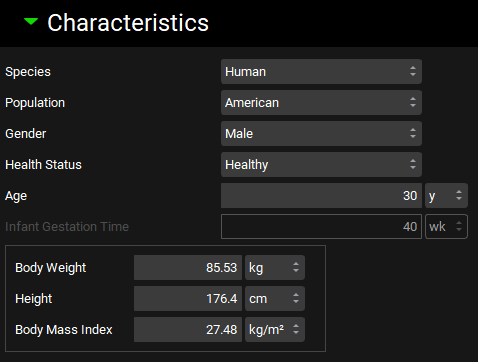
Physiologies view, Characteristics panel
Input/Option | Description |
Species | Selects the species for the physiology: Human, Rat, Mouse, Dog, Minipig, Swine, Rhesus or Cynomolgus Monkey, Rabbit, or Cat. |
Population | Selects the ethnicity for the physiology: American, Chinese, or Japanese. Applicable only for human physiologies. |
Gender | Selects the gender for the physiology. Applicable only for human physiologies. |
Health Status | Selects the health status for the physiology. This can include healthy (baseline), disease states such as renal or hepatic impairment, or pregnancy for females. Selecting pregnant will enable additional options for fetal characteristics. Applicable only for human physiologies. |
Age | The age for the physiology. For human physiologies, both the value and the units (days, weeks, months, years) can be edited. |
Infant Gestation Time | The gestational age, in weeks, for the physiology. Applicable only for infant human physiologies. This field will be enabled only if the age is less than one year. The value can be edited. |
Body Weight | The total weight (mass) of the physiology. The value and the units (g, kg) can be edited. Edits to this field will also trigger a recalculation of BMI for human physiologies. |
Height | The height of the physiology. Applicable only for human physiologies. The value and the units (in, cm, m) can be edited. Edits to this field will also trigger a recalculation of BMI for human physiologies. |
Body Mass Index | The body mass index (BMI) for the physiology. Applicable only for human physiologies. The value and the units (kg/m2, g/m2) can be edited. Edits to this field will also trigger a recalculation of height for human physiologies. |
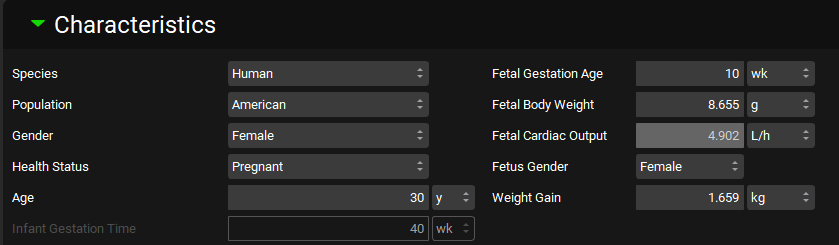
Physiologies view, Characteristics panel (Fetal Characteristics)
Input/Option | Description |
Fetal Gestation Age | The gestational age for the fetus. Both the value and the units (weeks, months, years) can be edited. |
Fetal Body Weight | The weight (mass) of the fetus. Both the value and the units (g, kg, oz, lb) can be edited. |
Fetal Cardiac Output | The cardiac output, in L/h, for the fetus. This value is calculated based on other fetal parameters and cannot be edited. |
Fetus Gender | Selects the gender of the fetus. |
Weight Gain | The maternal weight (mass) gain as a function of pregnancy and fetal development. This added weight is also reflected in the maternal physiology’s total body weight field. The value and the units (g, kg, lb) can be edited. |
Population Estimates for Age-Related Physiology (PEAR) Panel
The Population Estimates for Age-Related Physiology (PEAR) panel is used to create and/or update a PEAR physiology based on the characteristics set in the Characteristics panel. This panel displays the cardiac output and body fat percentage for the physiology, as well as a table detailing the size (volume), perfusion, and relative proportion of each tissue in the PEAR physiology. This panel will be enabled only if the PBPKPlus™ module is licensed.
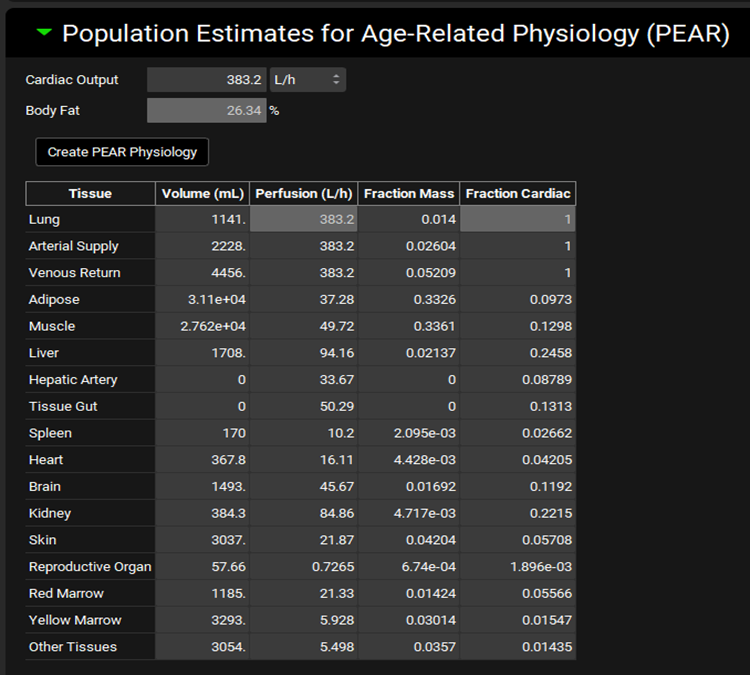
Physiologies view, Population Estimates for Age-Related Physiology (PEAR) panel
Input/Option | Description |
Cardiac Output | The cardiac output for the selected physiology. This initial calculated value is based on the characteristics defined above. Both the value and the units (L/h, L/min, mL/min, mL/s) can be edited. |
Body Fat | The body fat, in percent, of the physiology. This is calculated based on the size of Adipose tissue relative to other tissues in the table below and cannot be edited. |
Create PEAR Physiology | Creates a PEAR Physiology for the selected physiology, based on the characteristics above, if none exists yet. If a PEAR physiology already exists, clicking this button will reset cardiac output and all tissue physiological parameter to their default values, based on the characteristics above. |
PEAR Physiology Table | This table contains information on the relative proportions of all tissues in the PEAR physiologies, including their size (volume) and degree of perfusion. |
Tissue | Indicates the tissue for which parameters are displayed. There are 13 tissues by default in GastroPlus®, along with four entries for circulatory compartments (Arterial Supply, Venous Return, Hepatic Artery, and Tissue Gut [represents gut perfusion connected to the ACAT model]). However, additional entries may be present for pregnant physiologies. |
Volume | The volume of the tissue. Both the value and the units (L, mL) can be edited. Editing a tissue volume will update the Fraction Mass of this and other tissues. |
Perfusion | The perfusion (blood flow) of the tissue. Both the value and the units (L/h, L/min, mL/min, mL/s) can be edited. Lung, Arterial Supply, and Venous Return have a perfusion equal to cardiac output by definition. Editing a tissue perfusion value will update the Fraction Cardiac of this and other tissues. |
Fraction Mass | The fraction of the tissue mass as compared to the total mass of the physiology. The value can be edited. Editing this value will rebalance the Volume and Fraction Mass for all tissues. |
Fraction Cardiac | The fraction of the tissue perfusion as compared to cardiac output. The value can be edited. Editing this value will rebalance the Perfusion and Fraction Cardiac for all tissues. |
Physiomolecular Properties Selection Pop-up
Physiomolecular properties are properties that depend on both a compound and a physiology (physiology + molecule = physiomolecular). Examples of physiomolecular properties include the fraction unbound in plasma, tissue type (permeability or perfusion limited), tissue partition coefficients, intrinsic clearance in a tissue, fraction unbound in enterocytes, and blood to plasma concentration ratio, among others. These are commonly thought of as properties of the compound, but they are also specific to the physiology—a given compound may have different protein binding in humans versus rats, for example.
Every time a new compound-physiology pair is selected, physiomolecular properties must be set up for that pair. When a compound and a physiology are selected at the top of the Physiologies or Pharmacokinetics views, if the physiomolecular properties have not yet been defined, the physiomolecular properties selection window will pop-up, enabling the existing physiomolecular properties to be copied, or to be set to the default values. However, when a compound or a physiology is copied, the physiomolecular properties for that asset are copied with it.
The current compound and physiology are displayed at the top of the pop-up window, as well as a drop-down for selecting the species. Below that is a list of physiologies for that species that have already been paired with the indicated compound, from which the existing physiomolecular properties may be copied to the new physiology. Alternatively, the default values may be used instead of copying properties over. In all cases, users can edit the specific values in the interface at any point.
For example, in the below figure, the physiology “New Human” has just been created, with CompoundX already selected as the current compound at the top of the view. Because “New Human” has not been paired with any compound yet, the Physiomolecular Properties Selection pop-up is triggered. The option is provided, for human species, to copy properties over from either the “30y 75.4kg Human American Female” or “30y 85.5kg Human American Male” physiology, both of which have already been paired with CompoundX and thus have an existing set of physiomolecular properties. Selecting “30y 75.4kg Human American Female”, for example, would copy the physiomolecular properties for the “30y 75.4kg Human American Female—CompoundX” pair to the “New Human—CompoundX” pair.
Physiomolecular Properties Selection pop-up
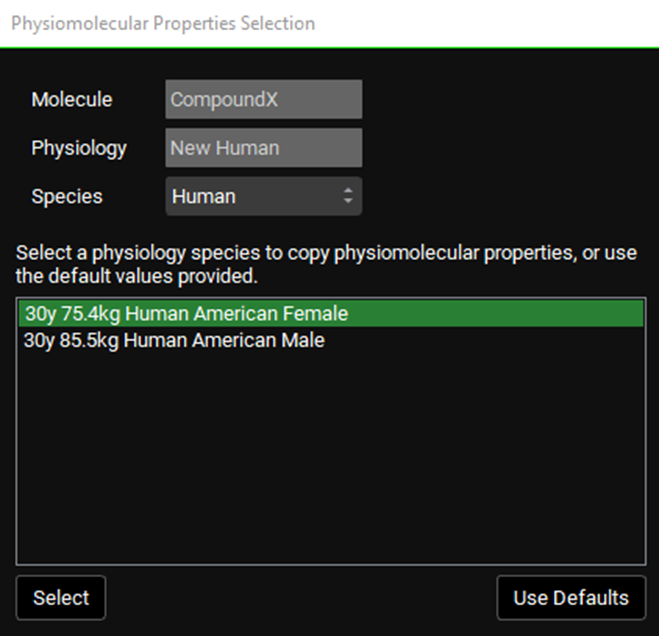
Input/Option | Description |
Molecule | The currently selected compound. Based on the compound selected at the top of the view. |
Physiology | The currently selected physiology. Based on the physiology selected at the top of the view (which may also be the physiology just created, in certain workflows). |
Species | A drop-down. Selects the species for which physiologies will be displayed in the area below. Only physiologies of that species which have been paired with the compound indicated above will appear below. |
Physiology Selector Area | Displays, and allows selection of, existing physiologies that have physiomolecular properties for the compound indicated above. A single entry from this list may be selected for copying the properties to the new compound-physiology pair. Click on the physiology’s name to select it. Selected items will be highlighted in green. |
Select | Confirms the above selection and copies the physiomolecular properties from the indicated compound-physiology pair to the new compound-physiology pair. |
Use Defaults | Sets the physiomolecular properties for new compound-physiology pair to the default values, rather than copying existing properties. Default values are typically either 1 or 0, depending on the parameter. |
The physiomolecular properties selection pop-up will be triggered on the Pharmacokinetics view or on the Physiologies view with the Population Estimates for Age-Related Physiology (PEAR), Gastrointestinal, or Bile (Enterohepatic Circulation) panels expanded. The compound and physiology selection can be changed freely without raising this pop-up when on the Physiologies view with those panels collapsed.
Gastrointestinal Panel
The Gastrointestinal panel contains information on the gut physiology and ACAT model parameters for the selected physiology. The top portion of the panel covers general ACAT settings. This is followed by an interactive ACAT diagram with sub-panels detailing the properties of each section. Lastly, there are tables summarizing the sectional ACAT parameters and enzyme and transporter distributions, only visible when these are included in the model.
General Settings
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel (General ACAT Settings)
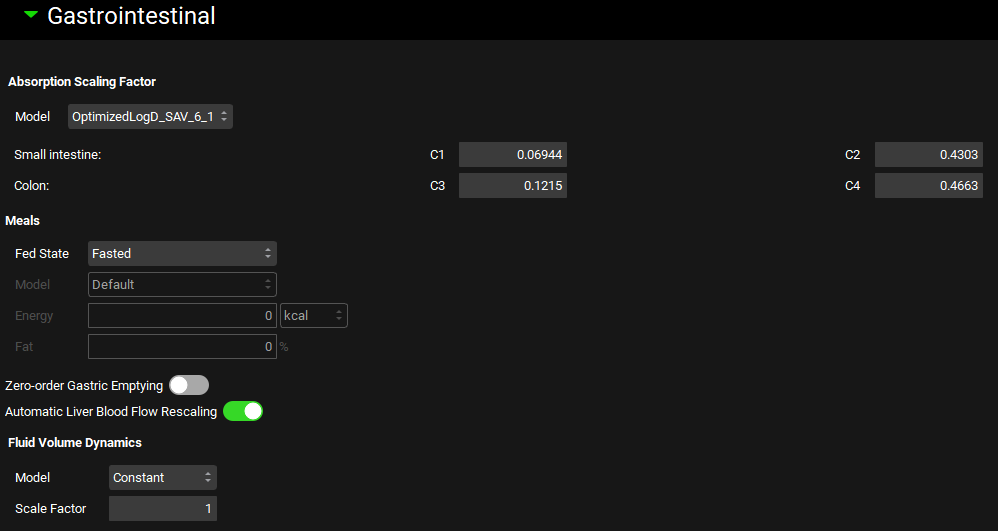
Input/Option | Description |
Absorption Scaling Factor | Settings for the Absorption Scaling Factor (ASF) models for the compound-physiology pair. Different ASF models can be set up for a given compound-physiology pair, with the specific model used for a given simulation being selected during simulation setup. |
Model | A drop-down. Selects the ASF model to view. |
C1-4 | The C1, C2, C3, and C4 coefficients for use in ASF calculations for the selected ASF model. The values can be edited. These values are not used for User Defined ASF models. |
Meals | Settings for the changes in gut physiology based on feeding status. |
Fed State | Selects whether the physiology is in the fasted or fed state. Fasted is the default option. Switching between fed and fasted states will automatically update the liver blood flow (in both compartmental and PBPK models) for the current physiology to account for increased portal circulation in the fed state. |
Model | A drop-down. Selects the meal type. Only enabled if Fed State is set to fed. The meal type will determine the energy (calories) and fat percentage for the meal, or, for User Defined, enable editing of those fields. |
Energy | The energy, in kcal, of the meal. If the meal type is set to User Defined, this value can be edited. For all other meal types, this value is shown for informational purposes and cannot be edited. |
Fat | The fat content, as a percent, of the meal. If the meal type is set to User Defined, this value can be edited. For all other meal types, this value is shown for informational purposes and cannot be edited. |
Zero Order Gastric Emptying | A toggle. Controls whether drug transit from the stomach to the duodenum (via gastric emptying) will be zero order (constant rate) or follow a distribution around mean transit time as in transit between other gut sections. The default setting for the fed state is zero order. |
Automatic Liver Blood Flow Rescaling | A toggle. Controls whether liver blood flow will be automatically scaled when the Fed State is updated. On by default. To prevent automatic liver blood flow scaling, turn the toggle off prior to switching the Fed State. |
Fluid Volume Dynamics | Settings for dynamic luminal fluid volume. In constant fluid volume models, luminal fluid volume will not change over the course of the simulation. Dynamic fluid volume models will have the luminal fluid volume change over the course of the simulation as a function of fluid secretion and reabsorption. |
Model | A drop-down. Selects the fluid volume model: Constant or Dynamic. |
Scale Factor | Scales the total amount of fluid by adjusting the rates of fluid secretion across gut sections. This value does not impact the rate of reabsorption. Changes to this value will affect the Fluid Distribution percentages above, as well as the fluid secretion rate in the ACAT Table below. This value can be edited only if the Fluid Volume model is set to dynamic. A higher number will result in more fluid being secreted. A scale factor of 1 uses values based on the MRI measurements of stomach and small intestine fluid volume in the fasted state 1 . |
The Absorption Scaling Factor model selected here allows users to preview ASF values for the compound-physiology pair based on the ASF model type and the C1-4 values. In the case of a User Defined ASF model, the ASF values may also be set here. However, the intended model type must be selected during simulations setup (see ACAT Model sub-panel)—changing the model here does not automatically update simulations.
ACATPlus™ toggle
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACAT™ Model sub-panel

Input/Option | Description |
ACATPlus™ Model | A toggle. Switched off by default. If activated, the ACATPlus™ model will be used for the selected physiology. Refer to ACATPlus™ Model sub-panel for more information. |
ACAT diagram with ACATPlus™ Model inactive
Below the general settings is the interactive ACAT diagram, which shows the gut sections in order, transit between them, and their connection to the systemic model. Each individual section can be selected to display detailed information on the section, in the four sub-panels to the right.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel (Interactive Diagram)
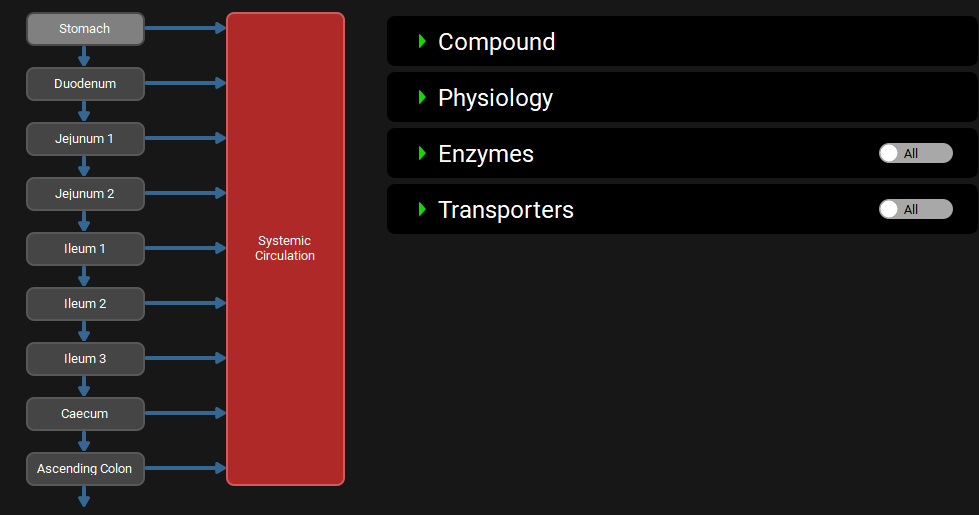
Compound sub-panel
The compound sub-panel contains information on compound properties—sectional permeability and fraction unbound in enterocytes—in the selected gut section. These properties are linked to the compound-physiology pair selected at the top of the Physiologies view.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Compound sub-panel
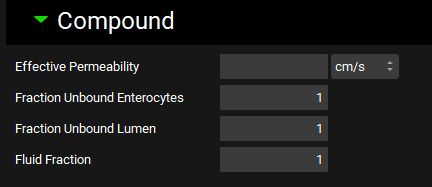
Input/Option | Description |
Effective Permeability | The effective permeability (Peff) of this compound in this physiology, for the selected gut section. The value and the units (cm/s, nm/s, µm/s, mm/s) can be edited. If a value, including a value of 0, is entered here, it will override the converted Peff for the compound (see Permeability panel and Permeability sub-panel). The value entered will be used directly in the simulation without undergoing further conversion. |
Fraction Unbound Enterocytes | The fraction unbound in enterocytes of this compound in this physiology, for the selected gut section. The value can be edited. If the Single Fraction Unbound in Enterocytes option below the diagram is toggled on, this field will be disabled. However, the previous value will be retained, and will be available again if the Single Fraction Unbound in Enterocytes option is toggled off. |
Fraction Unbound Lumen | The fraction unbound in lumen of this compound in this physiology, for the selected gut section. The value can be edited. |
Fluid Fraction | The fluid distribution, as a fraction, for the selected gut section. The default value is 1 for the stomach, 0.4 for small intestine compartments and 0.1 for colon compartments. The value can be edited. |
Physiology sub-panel
The physiology sub-panel contains information about physiological parameters for the selected gut section. These properties are linked to the physiology selected at the top of the Physiologies view and the inputs shown in the sub-panel updated based on the gut section selected.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Physiology sub-panel, Duodenum selected
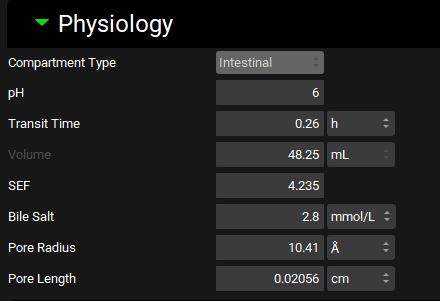
Input/Option | Description |
Compartment Type | Indicates whether the compartment type of the selected gut section is Stomach, Intestinal, or Colon. This field is for informational purposes and cannot be edited. |
pH | The pH in the selected gut section. The value can be edited. |
Transit Time | The average transit time through the selected gut section. The value and the units (h, s, min) can be edited. |
Volume | The total volume of the selected gut section. For the stomach, the value and the units (mL, L) can be edited. For intestinal and colonic sections, this value is the cylindrical volume calculated from the length and radius of the gut section (see ACAT table) and cannot be edited. |
Length | The length of the selected gut section. The units (cm, mm, m) can be edited. Available for Caecum and Ascending Colon only. |
Radius | The radius of the selected gut section. The units (cm, mm, m) can be edited. Available for Caecum and Ascending Colon only. |
SEF | The surface area enhancement factor for the indicated gut section. The value can be edited. This value is used in the optimized logD SA/V ASF models. A higher value corresponds to a higher ASF. |
Bile Salt | The bile salt concentration in the selected gut section. The value and the units (mmol/L, µmol/L) can be edited. Available for intestinal sections only. |
Pore Radius | The average radius of paracellular pores in the selected gut section. The value and the units (Å, nm, µm) can be edited. |
Pore Length | The average length of paracellular pores in the selected gut section. The value and the units (cm, mm, µm) can be edited. |
Enzymes sub-panel
The Enzymes sub-panel displays information on enzymes expressed in the selected gut section, for the physiology selected at the top of the Physiologies view. Enzymes can be filtered based on those assigned to the compound for the specific Physiology (See Enzyme Kinetics panel) using the All/Active toggle.
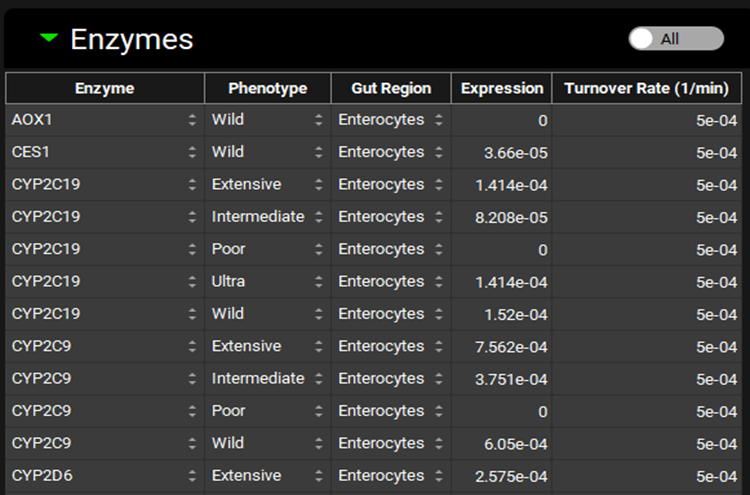
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Enzymes Sub-panel (All Enzymes)
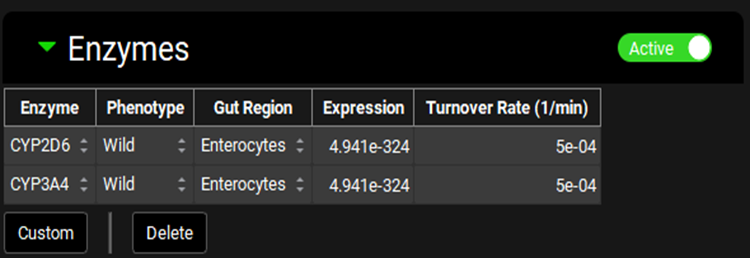
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Enzymes sub-panel (Active Enzymes)
Input/Option | Description |
Enzyme | Indicates the enzyme for which expression information is shown. Different enzymes may be selected using the drop-down. |
Phenotype | The phenotype of the indicated enzyme. A different phenotype may be selected using the drop-down (Wild, Poor, Intermediate, Extensive, Ultra). However, for enzymes where the change in Expression is not built-in, the expression will need to be updated manually. |
Gut Region | Indicates the region, enterocytes or gut lumen, in which the enzyme is expressed. A different location may be selected using the drop-down. |
Expression | The relative expression of the enzyme in the selected gut section. This value is multiplied by the gut Vmax in the Enzyme Kinetics table to get the final Vmax used in the simulation. The value can be edited. |
Turnover Rate | The turnover rate, of the indicated enzyme in the selected gut section. The value and the units can be edited (1/min, 1/h, 1/s). |
All/Active | A toggle. Controls whether the enzymes shown will be filtered based on the compound selected at the top of the Physiologies view (see Enzyme Kinetics panel). |
Custom | Add a custom enzyme for the species of the current physiology. Once the custom enzyme is created, it will be added automatically as a row to the table. It will also be available thereafter in the enzyme drop-down for selection. Custom enzymes added here must still be assigned to the intended compound using the Enzyme Kinetics table on the Compounds view (see Enzyme Kinetics panel). |
Delete | Delete the selected row from the table. Hold [CTRL]-key and click anywhere in the row to select it for deletion. |
When adding or changing enzymes, the table will automatically sort alphabetically based on enzyme name. If the filter is set to Active, the enzyme also needs to be assigned to the compound in the Enzyme Kinetics table in the Compounds view before it will be displayed in this table.
Transporters sub-panel
The Transporters sub-panel displays information on transporters expressed in the selected gut section, for the physiology selected at the top of the Physiologies view. Transporters can be filtered based on those assigned to the compound (See Transporter Kinetics panel) using the All/Active Toggle.
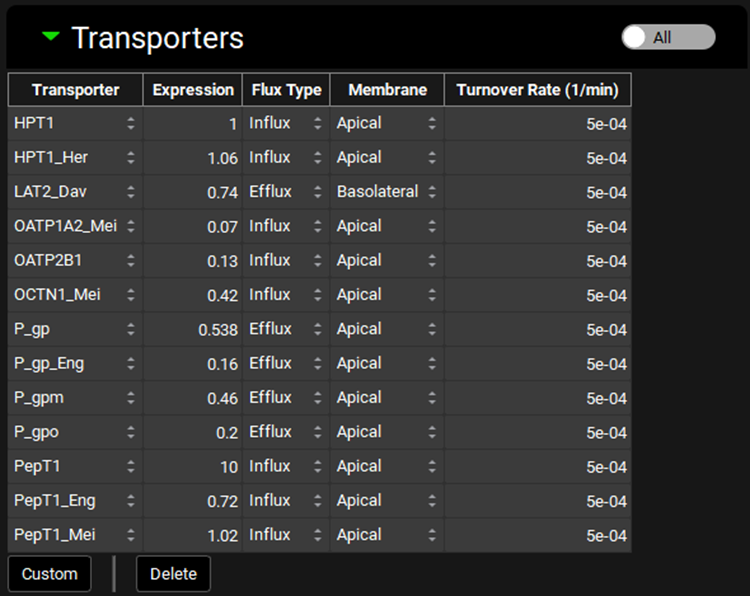
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Transporter sub-panel
Input/Option | Description |
Transporter | Indicates the transporter for which expression information is shown. Different transporters may be selected using the drop-down. |
Expression | The relative expression of the transporter in the selected gut section. This value is multiplied by the gut Vmax in the Transporter Kinetics table to get the final Vmax used in the simulation. The value can be edited. |
Flux Type | Indicates the flux direction (influx or efflux) for the transporter. Flux type may be changed using the drop-down. |
Membrane | Indicates the membrane location (apical or basolateral) for the transporter. Membrane location may be changed using the drop-down. |
Turnover Rate | The turnover rate, of the indicated transporter in the selected gut section. The value and the units can be edited (1/min, 1/h, 1/s). |
All/Active | A toggle. Controls whether the transporters shown will be filtered based on the compound selected at the top of the Physiologies view (see Transporter Kinetics panel). |
Custom | Add a custom transporter for the species of the current physiology. Once the custom transporter is created, it will be added automatically as a row to the table. It will also be available thereafter in the transporter drop-down for selection. Custom transporters added here must still be assigned to the intended compound using the Transporter Kinetics table on the Compounds view. |
Delete | Delete the selected row from the table. Hold [CTRL]-key and click anywhere in the row to select it for deletion. |
ACAT table with ACATPlus™ Model inactive
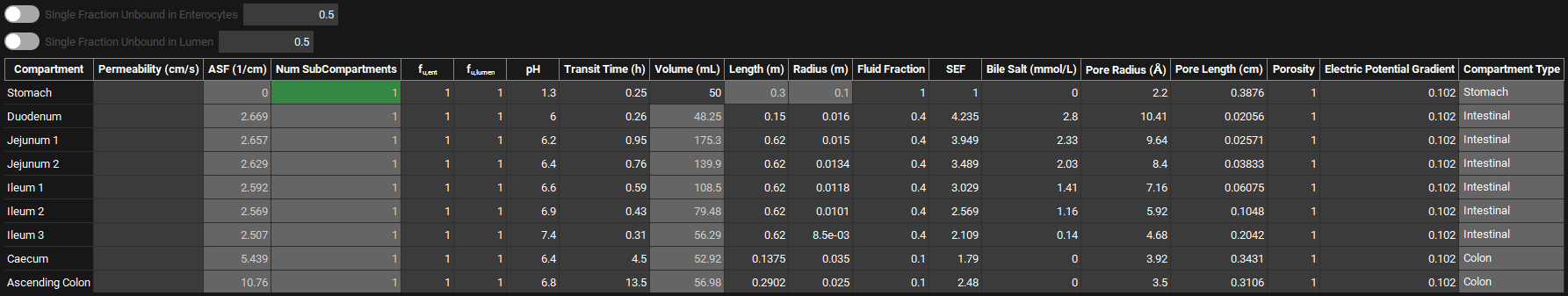
The ACAT table contains a summary of all parameters for each gut section. All information within is linked to the physiology selected at the top of the Physiologies view. Additionally, permeability, ASF, and fraction unbound in enterocytes (fu,ent) are also linked to the compound selected at the top of the view.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACAT table
Input/Option | Description |
Single Fraction Unbound in Enterocytes (Toggle) | A toggle. Controls whether a single fraction unbound value will be used for enterocyte binding in all gut sections. |
Single Fraction Unbound in Enterocytes (Value) | The value to be used as the Single Fraction Unbound in Enterocytes. This value will be applied to all gut sections with the exception of stomach (reflected in the ACAT Table below) if the adjacent toggle is on. The value can be edited. |
Single Fraction Unbound in Lumen (Toggle) | A toggle. Controls whether a single fraction unbound value will be used for lumen binding in all gut sections. |
Single Fraction Unbound in Lumen (Value) | The value to be used as the Single Fraction Unbound in Lumen. This value will be applied to all gut sections with the exception of stomach (reflected in the ACAT Table below) if the adjacent toggle is on. The value can be edited. |
Compartment | Identifies the gut section (compartment) to which all other information in the row applies. |
Permeability | The effective permeability (Peff) of this compound in this physiology, for the selected gut section. The value can be edited. The units (cm/s, nm/s, µm/s, mm/s) can be changed in the column header. If a value, including a value of 0, is entered here, it will override the converted Peff for the compound (see Permeability panel and Permeability sub-panel). The value entered will be used directly in the simulation to define the absorption in the specific gut section without undergoing further conversion. To use the compound Peff as defined in the Simulation settings, the column must be left blank. |
ASF | The absorption scaling factor (ASF), in cm‑1, for the current compound-physiology pair in the indicated gut section. The value shown is based on the ASF model type selected above. If a User Defined ASF model is selected, these values will be editable. For all other ASF models, these values will not be editable. |
Num SubCompartments | The number of sub-compartments for the selected gut section. The default value is 1 for the standard ACAT model and is not editable. |
fu,ent | The fraction unbound in enterocytes for the current compound-physiology pair in the indicated gut section. If Single Fraction Unbound in Enterocytes is toggled off, this value will be editable. If that option is toggled on, this field will reflect that value, and will not be editable. |
fu,lumen | The fraction unbound in lumen for the current compound-physiology pair in the indicated gut section. If Single Fraction Unbound in Lumen is toggled off, this value will be editable. If that option is toggled on, this field will reflect that value, and will not be editable. |
pH | The pH for the indicated gut section. The value can be edited. |
Transit Time | The mean transit time, in h, for the indicated gut section. The value can be edited. The units (s, min, h) can be selected in the column header. |
Volume | The volume of the indicated gut section. For the stomach, this represents fluid volume and is editable. For all other gut sections, this value represents the fluid volume of the gut section as calculated from cylindrical volume (based on section length and radius) using the fluid percentages above. For all gut section the units (mL, L) can be changed in the column header. |
Length | The length, in cm, of the indicated gut section. For intestinal and colonic sections, this value is used in the calculation of volume. The value can be edited for intestinal and colonic sections. |
Radius | The radius, in cm, of the indicated gut section. For intestinal and colonic sections, this value is used in the calculation of volume. The value can be edited for intestinal and colonic sections. |
Fluid Fraction | The fluid distribution, as a fraction, of the indicated gut section. The default value is 1 for the stomach, 0.4 for small intestine compartments and 0.1 for colon compartments. The value can be edited. |
SEF | The surface area enhancement factor for the indicated gut section. The value can be edited. This value is used in the optimized logD SA/V ASF models. A higher value corresponds to a higher ASF. |
Bile Salt | The bile salt concentration in the indicated gut section. The value can be edited. The units (mmol/L, µmol/L) can be changed in the column header. |
Pore Radius | The average radius of paracellular pores in the indicated gut section. The value and the units (Å, nm, µm) can be edited. |
Pore Length | The average length of paracellular pores in the indicated gut section. The value and the units (cm, mm, µm) can be edited. |
Porosity | The porosity of the indicated gut section. This value is used in conjunction with pore length and radius to calculate paracellular absorption. The value can be edited. |
Electrical Potential Gradient | The electrical potential gradient (EPG), in mV, of the indicated gut section. This value is used in the calculation of paracellular absorption of charged compounds. The value can be edited. |
Compartment Type | The compartment type (Stomach, Intestinal, Colon) of the indicated gut section. This is for informational purposes only and cannot be edited. |
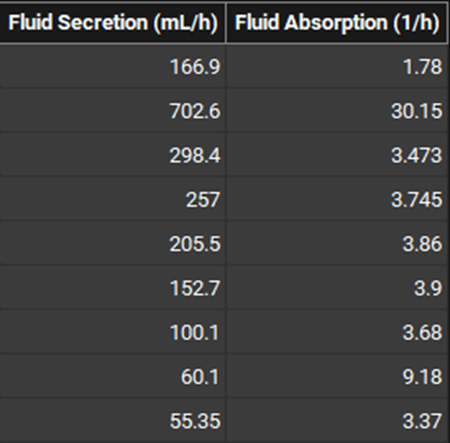
If the fluid volume model is set to dynamic, two additional columns will be appended to the ACAT Table, covering settings for the rates of fluid secretion and reabsorption.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACAT table (Dynamic Fluid Volume settings)
Input/Option | Description |
Fluid Secretion | The rate of fluid secretion for the indicated gut section, for use in dynamic fluid volume models. This column is only visible if the Fluid Volume Dynamics model is set to Dynamic. The value can be edited. The units (mL/h, L/h, mL/s) can be changed in the column header. |
Fluid Absorption | The rate of fluid reabsorption for the indicated gut section, for use in dynamic fluid volume models. This column is only visible if the Fluid Volume Dynamics model is set to Dynamic. The value can be edited. The units (1/h, 1/min, 1/s) can be changed in the column header. |
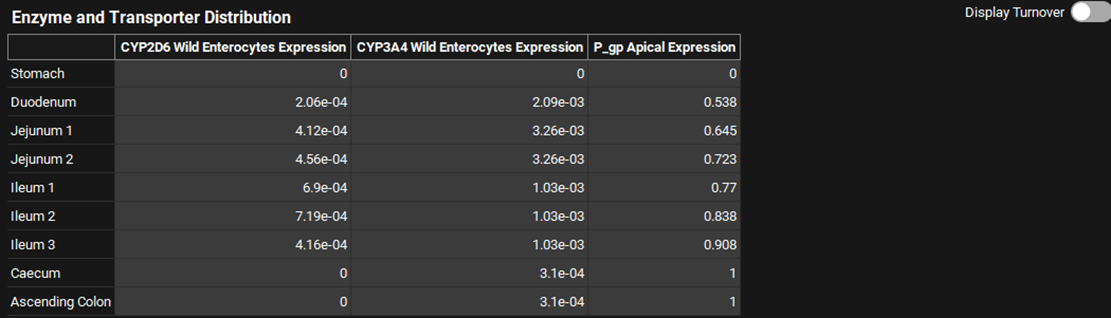
The Enzyme and Transporter Distribution table summarizes information on relative enzyme and transporter expressions across gut sections. Only enzymes and/or transporters already assigned to the compound selected at the top of the Physiologies view will be present. Those with unknown expression levels are shown with a default expression level of 1.
The table will always have one row per gut section. A column will be added for each relevant enzyme or transporter, with the protein name, phenotype, and location summarized in the column header. The relative expression (distribution) values in the table can be edited.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Enzyme and Transporter Distribution Panel
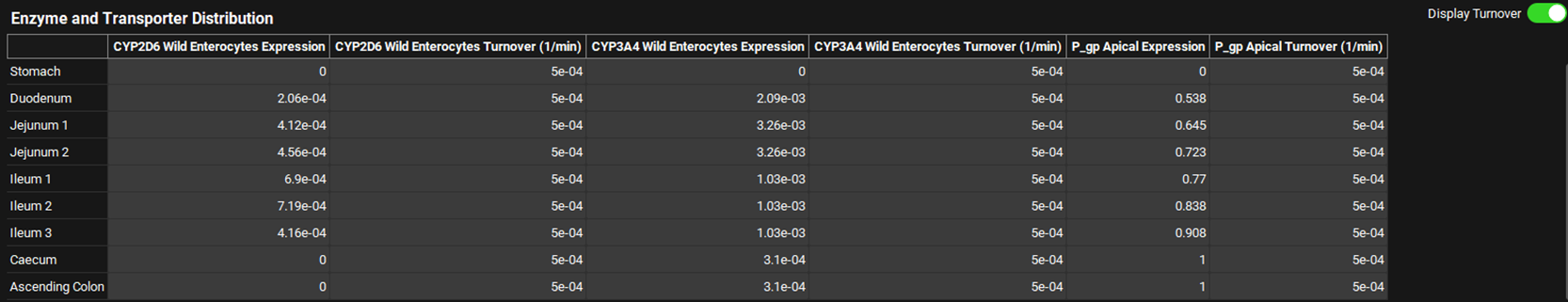
The Display Turnover toggle when on, will add columns displaying the Turnover (in 1/min) of each enzyme and/or transporter already assigned to the compound selected at the top of the Physiologies view. The toggle is off by default.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Enzyme and Transporter Distribution Panel - Display Turnover toggle On
ACATPlus™ Model sub-panel
ACATPlus™ enhances the traditional ACAT model by enabling the simulation of drug distribution within gut tissue and incorporating additional colon segments. This extension supports the evaluation of gastrointestinal (GI) local acting compounds and controlled-release formulations that target colonic absorption.
The ACATPlus™ function can be enabled by turning on the ACATPlus™ Model toggle. The ACATPlus™ Model input sub-panel lists the input variables specifically for ACATPlus™ and is only displayed when the toggle is on.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACATPlus™ Model sub-panel
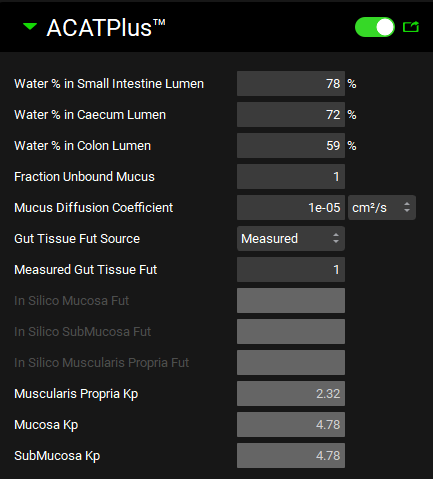
Input/Option | Description |
ACATPlus™ Model (toggle) | A toggle. Switched off by default. If activated, the ACATPlus™ model will be used for the selected physiology. |
Water % in Small Intestine Lumen | The water concentration (%v/v) in luminal content in Small Intestine. It will be used to convert simulated luminal fluid concentration to luminal content concentration. The value can be edited. |
Water % in Caecum Lumen | The water concentration (%v/v) in luminal content in Caecum. It will be used to convert simulated luminal fluid concentration to luminal content concentration. The value can be edited. |
Water % in Colon Lumen | The water concentration (%v/v) in luminal content in Colon. It will be used to convert simulated luminal fluid concentration to luminal content concentration. The value can be edited. |
Fraction Unbound Mucus | The unbound fraction in mucus due to the binding to mucin for the current compound-physiology pair. The value can be edited. |
Mucus Diffusion Coefficient | The compound diffusivity coefficient in mucus. |
Gut Tissue Fut Source | A drop-down. Select Measured to input experimentally obtained fraction unbound in gut tissue or select Insilico to use the calculated fraction unbound in tissue based on tissue composition in gut. |
Measured Gut Tissue Fut | The value to be used in Mucosa, Submucosa, and Muscularis Propria as the fraction unbound in gut tissue. The value can be edited if Gut Tissue Fut Source (above) is set to Measured. |
In Silico Mucosa Fut | In Silico calculated Mucosa fraction unbound in tissue based on tissue composition in gut if the Gut Tissue Fut Source is set to Insilico. |
In Silico Submucosa Fut | In Silico calculated Submucosa fraction unbound in tissue based on tissue composition in gut if the Gut Tissue Fut Source is set to Insilico. |
In Silico Muscularis Propria Fut | In Silico calculated Muscularis Propria fraction unbound in tissue based on tissue composition in muscle if the Gut Tissue Fut Source is set to Insilico. |
Muscularis Propria Kp | In Silico calculated Muscularis Propria Kp based on tissue composition in muscle. |
Mucosa Kp | In Silico calculated Mucosa Kp based on tissue composition in gut. |
Submucosa Kp | In Silico calculated Submucosa Kp based on tissue composition in gut. |
ACAT diagram with ACATPlus™ Model active
Additional Colon Segments
For humans, the whole colon has been divided into ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon, and rectum. For mice and rats, the whole colon has been divided into colon 1, colon 2, colon 3, colon 4 and rectum. For dogs, the whole colon has been divided into ascending, transverse colon, descending colon 1, descending colon 2, and rectum. These additional segments are visible in the ACAT diagram when the ACATPlus™ Model toggle is active.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACATPlus™ Model diagram
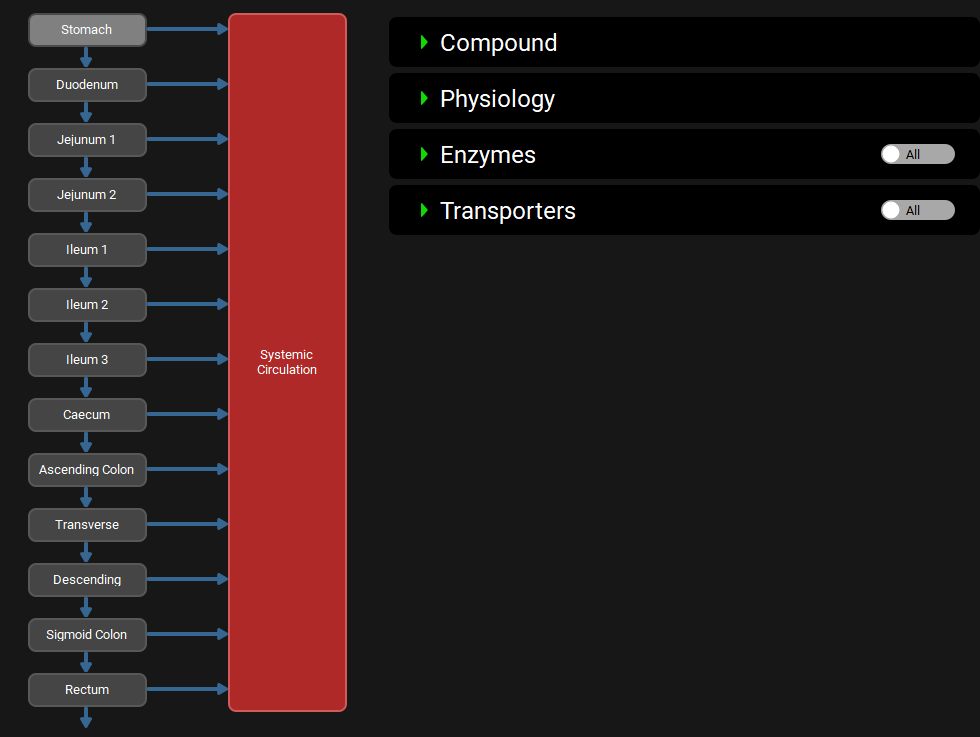
The additional parameters activated in the Physiology sub-panel when the ACATPlus™ Model toggle is activated are described below. Other parameters are described in the following section: ACAT diagram with ACATPlus™ Model inactive.
Physiology sub-panel
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, Physiology sub-panel, Ascending Colon selected, ACATPlus™ Model
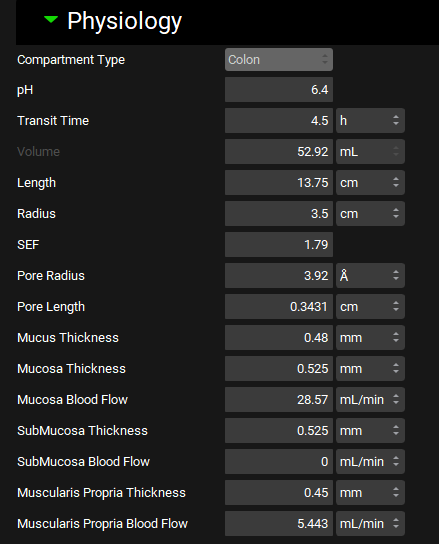
Parameters | Description |
Mucus Thickness | Thickness of the gut mucus layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
Mucosa Thickness | Tissue thickness of the gut mucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
Mucosa Blood Flow | Blood flow in the gut mucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mL/min, mL/h, mL/s) can be edited. |
SubMucosa Thickness | Tissue thickness of the gut submucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
SubMucosa Blood Flow | Blood flow in the gut submucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mL/min, mL/h, mL/s) can be edited. |
MuscularisPropria Thickness | Tissue thickness of the gut muscularis propria layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
MuscularisPropria Blood Flow | Blood flow in the gut muscularis propria layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mL/min, mL/h, mL/s) can be edited. |
ACAT table with ACATPlus™ Model active
The additional, species-specific, segments are displayed in the ACAT table. The parameters available are described in the ACAT table with ACATPlus™ Model inactive section, above. The only change to the columns is that the Num SubCompartments column is now editable for the colon segments.
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACAT Table, ACATPlus™ Model
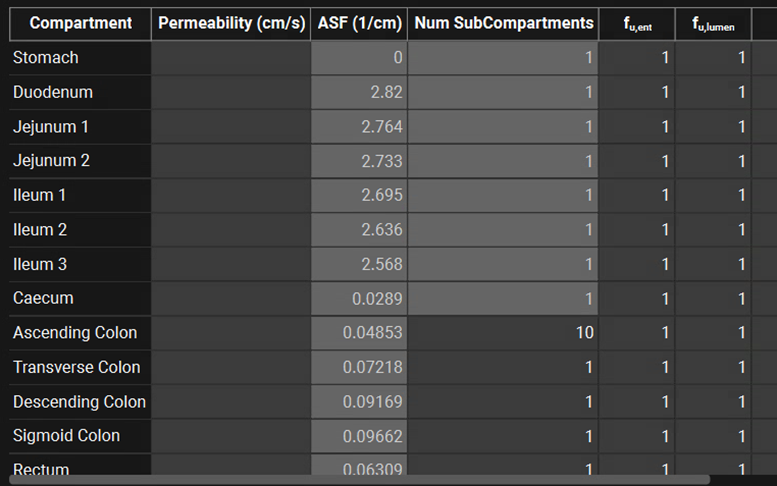

In order to simulate the slow transit in those colon segments, each segment can be further divided into multiple subcompartments. The maximum number of subcompartments is 10.
ACATPlus™ Physiological Parameters
Physiologies view, Gastrointestinal panel, ACATPlus™ Physiological Parameters table
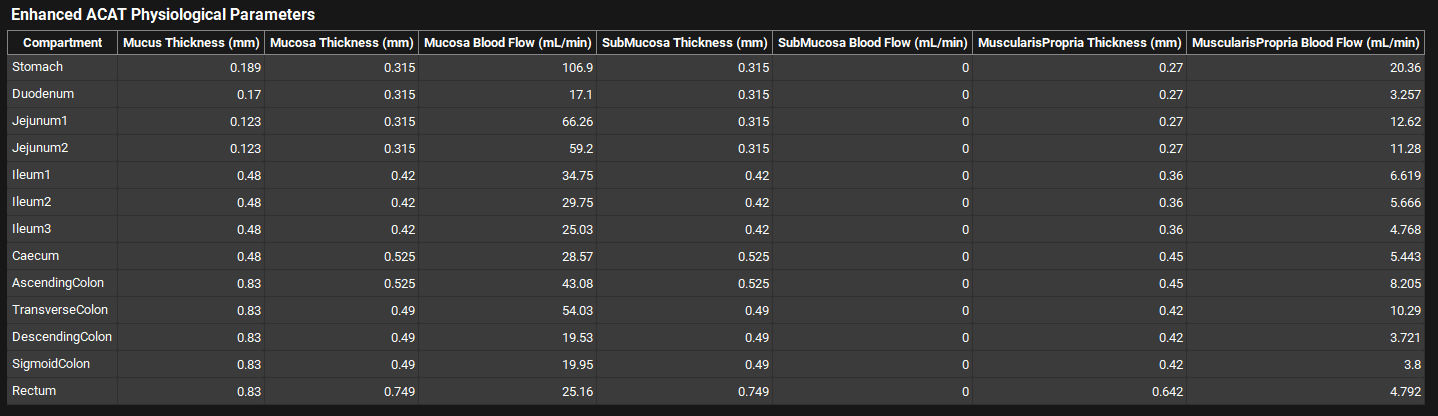
Parameters | Description |
Compartment | Identifies the gut section (compartment) to which all other information in the row applies. |
Mucus Thickness | Thickness of the gut mucus layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
Mucosa Thickness | Tissue thickness of the gut mucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
Mucosa Blood Flow | Blood flow in the gut mucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mL/min, mL/h, mL/s) can be edited. |
SubMucosa Thickness | Tissue thickness of the gut submucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
SubMucosa Blood Flow | Blood flow in the gut submucosa layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mL/min, mL/h, mL/s) can be edited. |
MuscularisPropria Thickness | Tissue thickness of the gut muscularis propria layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mm, cm, m) can be edited. |
MuscularisPropria Blood Flow | Blood flow in the gut muscularis propria layer of each GI segment. Value and units (mL/min, mL/h, mL/s) can be edited. |
Bile (Enterohepatic Circulation) Panel
The Bile (Enterohepatic Circulation) panel contains parameters for enterohepatic circulation (EHC) for the compound and physiology selected at the top of the Physiologies view. These parameters relate to the physiological and pharmacokinetic aspects of EHC; additional parameters for PBPK models are setup elsewhere. Passive apical flux via PStc is setup on the Pharmacokinetics view (see Compound sub-panel - Tissues), while active apical secretion via transporters needs to be setup in both the transporter kinetics table (see Physiology sub-panel - Tissues) and the transporter expression in the PBPK model (see Physiology sub-panel - Tissues). Settings controlling how EHC is applied to a simulation are set during simulation setup (see Compound Settings panel).
Physiologies view, Bile (Enterohepatic Circulation) panel
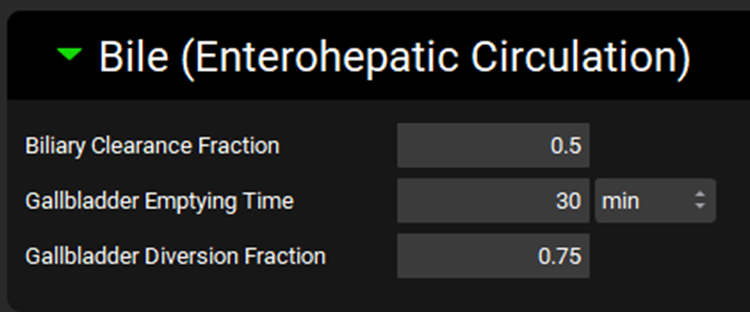
Input/Option | Description |
Biliary Clearance Fraction | The fraction of the clearance that is partitioned to bile. For compartmental models, this fraction is applied to general clearance. For PBPK models, it is applied to intrinsic clearance in the liver. This value is linked to the compound-physiology pair. The value can be edited. |
Gallbladder Emptying Time | The time over which the gallbladder will empty 90% of its contents after administration of a meal. Applies only to physiologies in which the Fed State is set to Fed. Affects the rate at which drug will transit from the gallbladder to the duodenum via the bile duct. This value is linked to the physiology only. Both the value and the units (h, min, s) can be edited although the default time of 30 min should rarely need to be changed. |
Gallbladder Diversion Fraction | The fraction of drug mass undergoing biliary clearance (via biliary clearance fraction, passive apical flux, or active apical efflux) which is stored in the gallbladder until gallbladder emptying. The remaining drug mass transits directly to the duodenum via the bile duct. This value is linked to the physiology only. The default value is 0.75 in the fasted state, and 0 in the fed state, except for rat, which is always 0. This value can be edited, although the default value should rarely need to be changed. |
Intramuscular Panel
For more information please see the Intramuscular (IM) and Subcutaneous (SubQ) section within the Additional Dosage Routes Guide.
Subcutaneous Panel
For more information please see the Intramuscular (IM) and Subcutaneous (SubQ) section within the Additional Dosage Routes Guide.
- Mudie, D.M., Murray, K., et al. (2014). “Quantification of gastrointestinal liquid volumes and distribution following a 240 mL dose of water in the fasted state.” Mol. Pharm. 11(9): 3039-3047.
